Trichothecin induces cell death in NF-κB constitutively activated human cancer cells via inhibition of IKKβ phosphorylation
- PMID: 23936501
- PMCID: PMC3731298
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071333
Trichothecin induces cell death in NF-κB constitutively activated human cancer cells via inhibition of IKKβ phosphorylation
Abstract
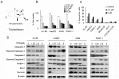
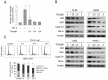
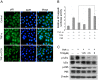
Constitutive activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is involved in tumorigenesis and chemo-resistance. As the key regulator of NF-κB, IKKβ is a major therapeutic target for various cancers. Trichothecin (TCN) is a metabolite isolated from an endophytic fungus of the herbal plant Maytenus hookeri Loes. In this study, we evaluated the anti-tumor activity of TCN and found that TCN markedly inhibits the growth of cancer cells with constitutively activated NF-κB. TCN induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells, activating pro-apoptotic proteins, including caspase-3, -8 and PARP-1, and decreasing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and survivin. Reporter activity assay and target genes expression analysis illustrated that TCN works as a potent inhibitor of the NF-κB signaling pathway. TCN inhibits the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα and blocks the nuclear translocation of p65, and thus inhibits the expression of NF-κB target genes XIAP, cyclin D1, and Bcl-xL. Though TCN does not directly interfere with IKKβ kinase, it suppresses the phosphorylation of IKKβ. Overexpression of constitutively activated IKKβ aborted TCN induced cancer cell apoptosis, whereas knockdown of endogenous IKKβ with siRNA sensitized cancer cells toward apoptosis induced by TCN. Moreover, TCN showed a markedly weaker effect on normal cells. These findings suggest that TCN may be a potential therapeutic candidate for cancer treatment, targeting NF-κB signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
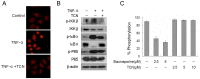
Similar articles
-
3-Formylchromone interacts with cysteine 38 in p65 protein and with cysteine 179 in IκBα kinase, leading to down-regulation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-regulated gene products and sensitization of tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 2;287(1):245-256. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274613. Epub 2011 Nov 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16926. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A111.274613 PMID: 22065587 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Targeting nuclear factor-kappa B activation pathway by thymoquinone: role in suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and enhancement of apoptosis.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Jun;6(6):1059-70. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2088. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18567808
-
A synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO-Me, inhibits IkappaBalpha kinase and enhances apoptosis induced by TNF and chemotherapeutic agents through down-regulation of expression of nuclear factor kappaB-regulated gene products in human leukemic cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15;12(6):1828-38. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2044. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16551868
-
Inhibition of tumor growth by NF-kappaB inhibitors.Cancer Sci. 2006 Oct;97(10):990-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00285.x. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16925581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Transcription Factor NF-κB as a Cancer Therapeutic Target and its Inhibitors as Cancer Treatment Options.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(21):4117-4132. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666201111142307. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33176636 Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer effect of the traditional Chinese medicine herb Maytenus compound via the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Sep;8(5):2130-2140. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.09.30. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116963 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Sex-Specific Dimorphism in Human Skeletal Stem Cells.Cells. 2023 Nov 22;12(23):2683. doi: 10.3390/cells12232683. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067111 Free PMC article.
-
Activities and metabolomics of Cordyceps gunnii under different culture conditions.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 12;13:1076577. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1076577. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36713217 Free PMC article.
-
DHRS2 mediates cell growth inhibition induced by Trichothecin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 10;38(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1301-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31291971 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic effect of novel Schiff based CdCl₂(C₁₄H₂₁N₃O₂) complex is mediated via activation of the mitochondrial pathway in colon cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 13;5:9097. doi: 10.1038/srep09097. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25764970 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

