Noncanonical control of vasopressin receptor type 2 signaling by retromer and arrestin
- PMID: 23935101
- PMCID: PMC3784700
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445098
Noncanonical control of vasopressin receptor type 2 signaling by retromer and arrestin
Abstract
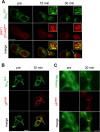
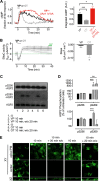
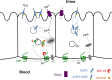
The vasopressin type 2 receptor (V2R) is a critical G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) for vertebrate physiology, including the balance of water and sodium ions. It is unclear how its two native hormones, vasopressin (VP) and oxytocin (OT), both stimulate the same cAMP/PKA pathway yet produce divergent antinatriuretic and antidiuretic effects that are either strong (VP) or weak (OT). Here, we present a new mechanism that differentiates the action of VP and OT on V2R signaling. We found that vasopressin, as opposed to OT, continued to generate cAMP and promote PKA activation for prolonged periods after ligand washout and receptor internalization in endosomes. Contrary to the classical model of arrestin-mediated GPCR desensitization, arrestins bind the VP-V2R complex yet extend rather than shorten the generation of cAMP. Signaling is instead turned off by the endosomal retromer complex. We propose that this mechanism explains how VP sustains water and Na(+) transport in renal collecting duct cells. Together with recent work on the parathyroid hormone receptor, these data support the existence of a novel "noncanonical" regulatory pathway for GPCR activation and response termination, via the sequential action of β-arrestin and the retromer complex.
Keywords: Arrestin; G Protein-coupled Receptors (GPCR); Kidney Metabolism; Membrane Trafficking; Signaling; V2R.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retromer terminates the generation of cAMP by internalized PTH receptors.Nat Chem Biol. 2011 May;7(5):278-84. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.545. Epub 2011 Mar 27. Nat Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21445058 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestin-dependent and -independent endosomal G protein activation by the vasopressin type 2 receptor.Elife. 2023 Oct 19;12:RP87754. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87754. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37855711 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of three vasopressin receptor 2 variants: an apparent polymorphism (V266A) and two loss-of-function mutations (R181C and M311V).PLoS One. 2013 Jun 6;8(6):e65885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065885. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762448 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical signaling of the PTH receptor.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Aug;33(8):423-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jun 16. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22709554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endosomal parathyroid hormone receptor signaling.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):C783-C790. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00452.2021. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35912987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β-Arrestin-independent endosomal cAMP signaling by a polypeptide hormone GPCR.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Mar;20(3):323-332. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01412-4. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 37749347 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of GPCR Signaling and Sorting from Very Early Endosomes via Opposing APPL1 Mechanisms.Cell Rep. 2017 Dec 5;21(10):2855-2867. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.023. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29212031 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIII. The parathyroid hormone receptors--family B G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(2):310-37. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009464. Pharmacol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25713287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Endosomal G-Protein-Coupled Receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Oct;39(10):879-891. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30180973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTH receptor-1 signalling-mechanistic insights and therapeutic prospects.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 Dec;11(12):712-24. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.139. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26303600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. (1990) β-Arrestin: a protein that regulates β-adrenergic receptor function. Science 248, 1547–1550 - PubMed
-
- Laporte S. A., Miller W. E., Kim K. M., Caron M. G. (2002) β-Arrestin/AP-2 interaction in G protein-coupled receptor internalization: identification of a β-arrestin binding site in β2-adaptin. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9247–9254 - PubMed
-
- Nelson C. D., Perry S. J., Regier D. S., Prescott S. M., Topham M. K., Lefkowitz R. J. (2007) Targeting of diacylglycerol degradation to M1 muscarinic receptors by β-arrestins. Science 315, 663–666 - PubMed
-
- Perry S. J., Baillie G. S., Kohout T. A., McPhee I., Magiera M. M., Ang K. L., Miller W. E., McLean A. J., Conti M., Houslay M. D., Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) Targeting of cyclic AMP degradation to β2-adrenergic receptors by β-arrestins. Science 298, 834–836 - PubMed
-
- Luttrell L. M., Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) The role of β-arrestins in the termination and transduction of G-protein-coupled receptor signals. J. Cell Sci. 115, 455–465 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

