NuMA phosphorylation by CDK1 couples mitotic progression with cortical dynein function
- PMID: 23921553
- PMCID: PMC3770949
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.172
NuMA phosphorylation by CDK1 couples mitotic progression with cortical dynein function
Abstract
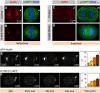
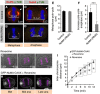
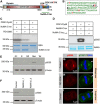
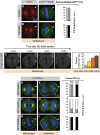
Spindle positioning and spindle elongation are critical for proper cell division. In human cells, an evolutionary conserved ternary complex (NuMA/LGN/Gαi) anchors dynein at the cortex during metaphase, thus ensuring correct spindle positioning. Whether this complex contributes to anaphase spindle elongation is not known. More generally, the mechanisms coupling mitotic progression with spindle behaviour remain elusive. Here, we uncover that levels of cortical dynein markedly increase during anaphase in a NuMA-dependent manner. We demonstrate that during metaphase, CDK1-mediated phosphorylation at T2055 negatively regulates NuMA cortical localization and that this phosphorylation is counteracted by PPP2CA phosphatase activity. We establish that this tug of war is essential for proper levels of cortical dynein and thus spindle positioning during metaphase. Moreover, we find that upon CDK1 inactivation in anaphase, the rise in dephosphorylated NuMA at the cell cortex leads to cortical dynein enrichment, and thus to robust spindle elongation. Our findings uncover a mechanism whereby the status of NuMA phosphorylation coordinates mitotic progression with proper spindle function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
NuMA phosphorylation dictates dynein-dependent spindle positioning.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(2):177-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.27040. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24241204 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
PP2A--B55γ counteracts Cdk1 and regulates proper spindle orientation through the cortical dynein adaptor NuMA.J Cell Sci. 2020 Jul 31;133(14):jcs243857. doi: 10.1242/jcs.243857. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32591484 Free PMC article.
-
NuMA phosphorylation dictates dynein-dependent spindle positioning.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(2):177-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.27040. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24241204 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
NuMA interacts with phosphoinositides and links the mitotic spindle with the plasma membrane.EMBO J. 2014 Aug 18;33(16):1815-30. doi: 10.15252/embj.201488147. Epub 2014 Jul 4. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 24996901 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NuMA in vertebrate cells: review of an intriguing multifunctional protein.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1137-46. doi: 10.2741/1868. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146802 Review.
-
Mechanisms of spindle positioning: cortical force generators in the limelight.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Dec;25(6):741-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23958212 Review.
Cited by
-
Pins is not required for spindle orientation in the Drosophila wing disc.Development. 2016 Jul 15;143(14):2573-81. doi: 10.1242/dev.135475. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Development. 2016. PMID: 27287805 Free PMC article.
-
PP2A--B55γ counteracts Cdk1 and regulates proper spindle orientation through the cortical dynein adaptor NuMA.J Cell Sci. 2020 Jul 31;133(14):jcs243857. doi: 10.1242/jcs.243857. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32591484 Free PMC article.
-
NuMA1 promotes axon initial segment assembly through inhibition of endocytosis.J Cell Biol. 2020 Feb 3;219(2):e201907048. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201907048. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31727776 Free PMC article.
-
NuMA regulates mitotic spindle assembly, structural dynamics and function via phase separation.Nat Commun. 2021 Dec 9;12(1):7157. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27528-6. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34887424 Free PMC article.
-
Astral microtubules control redistribution of dynein at the cell cortex to facilitate spindle positioning.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(7):1162-70. doi: 10.4161/cc.28031. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24553118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aist JR, Liang H, Berns MW (1993) Astral and spindle forces in PtK2 cells during anaphase B: a laser microbeam study. J Cell Sci 104(Pt 4): 1207–1216 - PubMed
-
- Axton JM, Dombradi V, Cohen PT, Glover DM (1990) One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell 63: 33–46 - PubMed
-
- Basto R, Pines J (2007) The centrosome opens the way to mitosis. Dev Cell 12: 475–477 - PubMed
-
- Cande WZ (1982) Inhibition of spindle elongation in permeabilized mitotic cells by erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)] adenine. Nature 295: 700–701 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

