Agonist-biased trafficking of somatostatin receptor 2A in enteric neurons
- PMID: 23913690
- PMCID: PMC3764777
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.496414
Agonist-biased trafficking of somatostatin receptor 2A in enteric neurons
Abstract
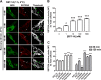
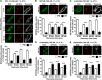
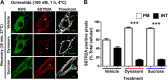
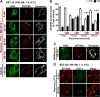
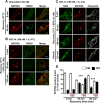
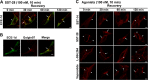
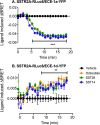
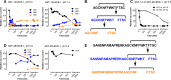
Somatostatin (SST) 14 and SST 28 activate somatostatin 2A receptors (SSTR2A) on enteric neurons to control gut functions. SST analogs are treatments of neuroendocrine and bleeding disorders, cancer, and diarrhea, with gastrointestinal side effects of constipation, abdominal pain, and nausea. How endogenous agonists and drugs differentially regulate neuronal SSTR2A is unexplored. We evaluated SSTR2A trafficking in murine myenteric neurons and neuroendocrine AtT-20 cells by microscopy and determined whether agonist degradation by endosomal endothelin-converting enzyme 1 (ECE-1) controls SSTR2A trafficking and association with β-arrestins, key regulators of receptors. SST-14, SST-28, and peptide analogs (octreotide, lanreotide, and vapreotide) stimulated clathrin- and dynamin-mediated internalization of SSTR2A, which colocalized with ECE-1 in endosomes and the Golgi. After incubation with SST-14, SSTR2A recycled to the plasma membrane, which required active ECE-1 and an intact Golgi. SSTR2A activated by SST-28, octreotide, lanreotide, or vapreotide was retained within the Golgi and did not recycle. Although ECE-1 rapidly degraded SST-14, SST-28 was resistant to degradation, and ECE-1 did not degrade SST analogs. SST-14 and SST-28 induced transient interactions between SSTR2A and β-arrestins that were stabilized by an ECE-1 inhibitor. Octreotide induced sustained SSTR2A/β-arrestin interactions that were not regulated by ECE-1. Thus, when activated by SST-14, SSTR2A internalizes and recycles via the Golgi, which requires ECE-1 degradation of SST-14 and receptor dissociation from β-arrestins. After activation by ECE-1-resistant SST-28 and analogs, SSTR2A remains in endosomes because of sustained β-arrestin interactions. Therapeutic SST analogs are ECE-1-resistant and retain SSTR2A in endosomes, which may explain their long-lasting actions.
Keywords: Arrestin; Endocytosis; Endothelin-converting Enzyme; Neurons; Neuropeptide; Receptor Recycling; Somatostatin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 degrades internalized somatostatin-14.Endocrinology. 2008 May;149(5):2200-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1628. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18276747 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 regulates trafficking and signalling of the neurokinin 1 receptor in endosomes of myenteric neurones.J Physiol. 2011 Nov 1;589(Pt 21):5213-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.214452. Epub 2011 Aug 30. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21878523 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-induced abnormalities in the subcellular localization and trafficking of the neurokinin 1 receptor in the enteric nervous system.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Aug 15;309(4):G248-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00118.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26138465 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular trafficking of somatostatin receptors.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 May 14;286(1-2):58-62. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.10.005. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18045773 Review.
-
Arresting inflammation: contributions of plasma membrane and endosomal signalling to neuropeptide-driven inflammatory disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Feb 1;41(1):137-43. doi: 10.1042/BST20120343. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23356273 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Endosomal G-Protein-Coupled Receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Oct;39(10):879-891. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30180973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Are Dynamic Regulators of Digestion and Targets for Digestive Diseases.Gastroenterology. 2019 May;156(6):1600-1616. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.266. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30771352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opioid receptor function is regulated by post-endocytic peptide processing.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 11;289(28):19613-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.537704. Epub 2014 May 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24847082 Free PMC article.
-
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Trafficking and Signalling in the Enteric Nervous System: The Past, Present and Future.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;891:145-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-27592-5_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27379642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation-associated changes in DOR expression and function in the mouse colon.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):G544-G559. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00025.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29927325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu B., Figini M., Emanueli C., Geppetti P., Grady E. F., Gerard N. P., Ansell J., Payan D. G., Gerard C., Bunnett N. (1997) The control of microvascular permeability and blood pressure by neutral endopeptidase. Nat. Med. 3, 904–907 - PubMed
-
- Lamberts S. W., van der Lely A. J., de Herder W. W., Hofland L. J. (1996) Octreotide. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 246–254 - PubMed
-
- Van Op den Bosch J., Adriaensen D., Van Nassauw L., Timmermans J. P. (2009) The role(s) of somatostatin, structurally related peptides and somatostatin receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. A review. Regul. Pept. 156, 1–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

