Molecular imaging reveals rapid reduction of endothelial activation in early atherosclerosis with apocynin independent of antioxidative properties
- PMID: 23908248
- PMCID: PMC3888901
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301710
Molecular imaging reveals rapid reduction of endothelial activation in early atherosclerosis with apocynin independent of antioxidative properties
Abstract
Objective: Antioxidative drugs continue to be developed for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Apocynin is an nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase inhibitor with anti-inflammatory properties. We used contrast-enhanced ultrasound molecular imaging to assess whether short-term apocynin therapy in atherosclerosis reduces vascular oxidative stress and endothelial activation
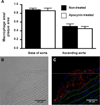
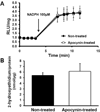
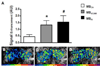
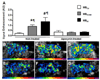
Approach and results: Genetically modified mice with early atherosclerosis were studied at baseline and after 7 days of therapy with apocynin (4 mg/kg per day IP) or saline. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound molecular imaging of the aorta was performed with microbubbles targeted to vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1; MB(V)), to platelet glycoprotein Ibα (MB(Pl)), and control microbubbles (MB(Ctr)). Aortic vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 was measured using Western blot. Aortic reactive oxygen species generation was measured using a lucigenin assay. Hydroethidine oxidation was used to assess aortic superoxide generation. Baseline signal for MBV (1.3 ± 0.3 AU) and MB(Pl )(1.5 ± 0.5 AU) was higher than for MBCtr (0.5 ± 0.2 AU; P<0.01). In saline-treated animals, signal did not significantly change for any microbubble agent, whereas short-term apocynin significantly (P<0.05) reduced vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and platelet signal (MBV: 0.3 ± 0.1; MBPl: 0.4 ± 0.1; MBCtr: 0.3 ± 0.2 AU; P=0.6 between agents). Apocynin reduced aortic vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 expression by 50% (P<0.05). However, apocynin therapy did not reduce reactive oxygen species content, superoxide generation, or macrophage content.
Conclusions: Short-term treatment with apocynin in atherosclerosis reduces endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression. This change in endothelial phenotype can be detected by molecular imaging before any measurable decrease in macrophage content and is not associated with a detectable change in oxidative burden.
Keywords: acetovanillone; atherosclerosis; microbubbles; molecular imaging; oxidative stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular Imaging of Platelet-Endothelial Interactions and Endothelial von Willebrand Factor in Early and Mid-Stage Atherosclerosis.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Jul;8(7):e002765. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.114.002765. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26156014 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging of inflammation and platelet adhesion in advanced atherosclerosis effects of antioxidant therapy with NADPH oxidase inhibition.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Jan 1;6(1):74-82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.975193. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23239832 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive ultrasound molecular imaging of the effect of statins on endothelial inflammatory phenotype in early atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058761. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554922 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the methoxyphenol apocynin, a vascular NADPH oxidase inhibitor, as a chemopreventative agent in the potential treatment of cardiovascular diseases.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;6(3):204-17. doi: 10.2174/157016108784911984. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18673160 Review.
-
Antioxidants and Atherosclerosis: Mechanistic Aspects.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 25;9(8):301. doi: 10.3390/biom9080301. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31349600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Atherosclerosis for Early Diagnosis and Therapeutic Evaluation through Leucocyte-like Multiple Targeted Microbubbles.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 14;8(7):1879-1891. doi: 10.7150/thno.22070. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556362 Free PMC article.
-
ICAM-1-carrying targeted nano contrast agent for evaluating inflammatory injury in rabbits with atherosclerosis.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 13;11(1):16508. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96042-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34389762 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Normalized Singular Spectrum Area as a Classifier for Molecularly Targeted Microbubble Adherence.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Sep;45(9):2493-2501. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.05.026. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31227262 Free PMC article.
-
Apocynin attenuates angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cells osteogenic switching via suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):83588-83600. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13193. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27835878 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Imaging of Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaques in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 9;17(9):1511. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091511. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27618031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singh U, Jialal I. Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. Pathophysiology. 2006;13:129–142. - PubMed
-
- Stolk J, Hiltermann TJ, Dijkman JH, Verhoeven AJ. Characteristics of the inhibition of nadph oxidase activation in neutrophils by apocynin, a methoxy-substituted catechol. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994;11:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Davidson BP, Yue Q, Belcik T, Xie A, Inaba Y, McCarty OJ, Tormoen GW, Zhao Y, Ruggeri ZM, Kaufmann BA, Lindner JR. Molecular imaging of inflammation and platelet adhesion in advanced atherosclerosis effects of antioxidant therapy with nadph oxidase inhibition. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:74–82. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Engels F, Renirie BF, Hart BA, Labadie RP, Nijkamp FP. Effects of apocynin, a drug isolated from the roots of picrorhiza kurroa, on arachidonic acid metabolism. FEBS Lett. 1992;305:254–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

