Extracellular proteome analysis of Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai
- PMID: 23895271
- PMCID: PMC3783971
- DOI: 10.1089/omi.2013.0043
Extracellular proteome analysis of Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai
Abstract
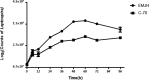
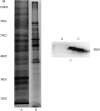
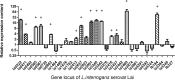
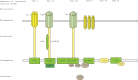
Abstract Leptospirosis is one of the most important zoonoses. Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai is a pathogenic spirochete that is responsible for leptospirosis. Extracellular proteins play an important role in the pathogenicity of this bacterium. In this study, L. interrogans serovar Lai was grown in protein-free medium; the supernatant was collected and subsequently analyzed as the extracellular proteome. A total of 66 proteins with more than two unique peptides were detected by MS/MS, and 33 of these were predicted to be extracellular proteins by a combination of bioinformatics analyses, including Psortb, cello, SoSuiGramN and SignalP. Comparisons of the transcriptional levels of these 33 genes between in vivo and in vitro conditions revealed that 15 genes were upregulated and two genes were downregulated in vivo compared to in vitro. A BLAST search for the components of secretion system at the genomic and proteomic levels revealed the presence of the complete type I secretion system and type II secretion system in this strain. Moreover, this strain also exhibits complete Sec translocase and Tat translocase systems. The extracellular proteome analysis of L. interrogans will supplement the previously generated whole proteome data and provide more information for studying the functions of specific proteins in the infection process and for selecting candidate molecules for vaccines or diagnostic tools for leptospirosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative subproteome analysis of three representative Leptospira interrogans vaccine strains reveals cross-reactive antigens and novel virulence determinants.J Proteomics. 2015 Jan 1;112:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Sep 6. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25201075
-
Genetic diversity among major endemic strains of Leptospira interrogans in China.BMC Genomics. 2007 Jul 1;8:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-204. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17603913 Free PMC article.
-
High-coverage proteome analysis reveals the first insight of protein modification systems in the pathogenic spirochete Leptospira interrogans.Cell Res. 2010 Feb;20(2):197-210. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.127. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 19918266
-
Pathogenesis of leptospirosis: the influence of genomics.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Nov 21;153(1-2):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.02.055. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21440384 Review.
-
Leptospirosis is an invasive infectious and systemic inflammatory disease.Biomed J. 2020 Feb;43(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.12.002. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32200953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
vWA proteins of Leptospira interrogans induce hemorrhage in leptospirosis by competitive inhibition of vWF/GPIb-mediated platelet aggregation.EBioMedicine. 2018 Nov;37:428-441. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.10.033. Epub 2018 Oct 15. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30337247 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Role of Type II Secretion in Bacterial Pathogenesis and Beyond.Infect Immun. 2017 Apr 21;85(5):e00014-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00014-17. Print 2017 May. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28264910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversification of the type IV filament superfamily into machines for adhesion, protein secretion, DNA uptake, and motility.PLoS Biol. 2019 Jul 19;17(7):e3000390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000390. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31323028 Free PMC article.
-
Applied Proteomics in 'One Health'.Proteomes. 2021 Jun 30;9(3):31. doi: 10.3390/proteomes9030031. Proteomes. 2021. PMID: 34208880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic Leptospira interrogans exoproteins are primarily involved in heterotrophic processes.Infect Immun. 2015 Aug;83(8):3061-73. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00427-15. Epub 2015 May 18. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25987703 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

