Contribution and regulation of TRPC channels in store-operated Ca2+ entry
- PMID: 23890115
- PMCID: PMC3824975
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407870-3.00007-X
Contribution and regulation of TRPC channels in store-operated Ca2+ entry
Abstract
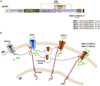
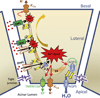
Store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) is activated in response to depletion of the endoplasmic reticulum-Ca(2+) stores following stimulation of plasma membrane receptors that couple to PIP2 hydrolysis and IP3 generation. Search for the molecular components of SOCE channels led to the identification of mammalian transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) family of calcium-permeable channels (TRPC1-TRPC7), which are all activated in response to stimuli that result in PIP2 hydrolysis. While several TRPCs, including TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC4, have been implicated in SOCE, the data are most consistent for TRPC1. Extensive studies in cell lines and knockout mouse models have established the contribution of TRPC1 to SOCE. Furthermore, there is a critical functional interaction between TRPC1 and the key components of SOCE, STIM1, and Orai1, which determines the activation of TRPC1. Orai1-mediated Ca(2+) entry is required for recruitment of TRPC1 and its insertion into surface membranes while STIM1 gates the channel. Notably, TRPC1 and Orai1 generate distinct patterns of Ca(2+) signals in cells that are decoded for the regulation of specific cellular functions. Thus, SOCE appears to be a complex process that depends on temporal and spatial coordination of several distinct steps mediated by proteins in different cellular compartments. Emerging data suggest that, in many cell types, the net Ca(2+) entry measured in response to store depletion is the result of the coordinated regulation of different calcium-permeable ion channels. Orai1 and STIM1 are central players in this process, and by mediating recruitment or activation of other Ca(2+) channels, Orai1-CRAC function can elicit rapid changes in global and local [Ca(2+)]i signals in cells. It is most likely that the type of channels and the [Ca(2+)]i signature that are generated by this process reflect the physiological function of the cell that is regulated by Ca(2+).
Keywords: Ca(2+) signaling; Cell function; Orai1; SOCE; STIM1; TRPC channels; TRPC1.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STIM-TRP Pathways and Microdomain Organization: Contribution of TRPC1 in Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry: Impact on Ca2+ Signaling and Cell Function.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;993:159-188. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57732-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28900914 Review.
-
Local Ca²+ entry via Orai1 regulates plasma membrane recruitment of TRPC1 and controls cytosolic Ca²+ signals required for specific cell functions.PLoS Biol. 2011 Mar;9(3):e1001025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001025. Epub 2011 Mar 8. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21408196 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TRPC Channels in Store-Operated Calcium Entry.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;898:87-109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-26974-0_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27161226 Review.
-
Contribution of TRPC1 and Orai1 to Ca(2+) entry activated by store depletion.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704:435-49. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0265-3_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21290310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPC channels function independently of STIM1 and Orai1.J Physiol. 2009 May 15;587(Pt 10):2275-98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.170431. Epub 2009 Mar 30. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19332491 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Store-operated interactions between plasmalemmal STIM1 and TRPC1 proteins stimulate PLCβ1 to induce TRPC1 channel activation in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Physiol. 2017 Feb 15;595(4):1039-1058. doi: 10.1113/JP273302. Epub 2016 Dec 7. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27753095 Free PMC article.
-
Tau-induced upregulation of C/EBPβ-TRPC1-SOCE signaling aggravates tauopathies: A vicious cycle in Alzheimer neurodegeneration.Aging Cell. 2020 Sep;19(9):e13209. doi: 10.1111/acel.13209. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 32815315 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 3 ion channel function in natural killer cells from Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis patients.Mol Med. 2018 Aug 14;24(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0046-1. Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30134818 Free PMC article.
-
SOCE induced calcium overload regulates autophagy in acute pancreatitis via calcineurin activation.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 19;9(2):50. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0073-9. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29352220 Free PMC article.
-
Classical Transient Receptor Potential 1 (TRPC1): Channel or Channel Regulator?Cells. 2014 Sep 29;3(4):939-62. doi: 10.3390/cells3040939. Cells. 2014. PMID: 25268281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmmed GU, Mehta D, Vogel S, Holinstat M, Paria BC, Tiruppathi C, et al. Protein kinase Calpha phosphorylates the TRPC1 channel and regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry in endothelial cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(20):20941–20949. - PubMed
-
- Almirza WH, Peters PH, van Zoelen EJ, Theuvenet AP. Role of Trpc channels, Stim1 and Orai1 in PGF(2alpha)-induced calcium signaling in NRK fibroblasts. Cell Calcium. 2012;51(1):12–21. - PubMed
-
- Ambudkar IS, Bandyopadhyay BC, Liu X, Lockwich TP, Paria B, Ong HL. Functional organization of TRPC-Ca2+ channels and regulation of calcium microdomains. Cell Calcium. 2006;40(5–6):495–504. - PubMed
-
- Ambudkar IS, Ong HL, Liu X, Bandyopadhyay BC, Cheng KT. TRPC1: The link between functionally distinct store-operated calcium channels. Cell Calcium. 2007;42(2):213–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

