SOCS proteins in development and disease
- PMID: 23885323
- PMCID: PMC3714205
SOCS proteins in development and disease
Abstract
Cytokine and growth factor signaling mediates essential roles in the differentiation, proliferation, survival and function of a number of cell lineages. This is achieved via specific receptors located on the surface of target cells, with ligand binding activating key intracellular signal transduction cascades to mediate the requisite cellular outcome. Effective resolution of receptor signaling is also essential, with excessive signaling having the potential for pathological consequences. The Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family of proteins represent one important mechanism to extinguish cytokine and growth factor receptor signaling. There are 8 SOCS proteins in mammals; SOCS1-7 and the alternatively named Cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein (CISH). SOCS1-3 and CISH are predominantly associated with the regulation of cytokine receptor signaling, while SOCS4-7 are more commonly involved in the control of Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling. Individual SOCS proteins are typically induced by specific cytokines and growth factors, thereby generating a negative feedback loop. As a consequence of their regulatory properties, SOCS proteins have important functions in development and homeostasis, with increasing recognition of their role in disease, particularly their tumor suppressor and anti-inflammatory functions. This review provides a synthesis of our current understanding of the SOCS family, with an emphasis on their immune and hematopoietic roles.
Keywords: JAK-STAT; SOCS; cytokine; development; disease; growth factor; immunity; receptor tyrosine; signalling.
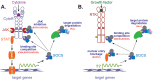
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS): inhibitors of the JAK/STAT pathway.Shock. 2002 Feb;17(2):83-90. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200202000-00001. Shock. 2002. PMID: 11837794 Review.
-
Differential roles of SOCS family members in EpoR signal transduction.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 Aug;22(8):853-60. doi: 10.1089/107999002760274863. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 12396724
-
A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling.Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):917-21. doi: 10.1038/43206. Nature. 1997. PMID: 9202125
-
SOCS proteins: negative regulators of cytokine signaling.Stem Cells. 2001;19(5):378-87. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.19-5-378. Stem Cells. 2001. PMID: 11553846 Review.
-
Functional conservation of suppressors of cytokine signaling proteins between teleosts and mammals: Atlantic salmon SOCS1 binds to JAK/STAT family members and suppresses type I and II IFN signaling.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Jul;45(1):177-89. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24582990
Cited by
-
The Neglected Suppressor of Cytokine Signalling (SOCS): SOCS4-7.Inflammation. 2024 Oct 26. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02163-7. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39460806 Review.
-
Identification of genetic variants or genes that are associated with Homoharringtonine (HHT) response through a genome-wide association study in human lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs).Front Genet. 2015 Jan 13;5:465. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00465. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25628645 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Analysis of Zebrafish socs4a: Impacts on the Notochord and Sensory Function.Brain Sci. 2022 Feb 10;12(2):241. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020241. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35204004 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Transcriptomic and microRNAomic Profiling Reveals Immune Mechanism for the Resilience to Soybean Meal Stress in Fish Gut and Liver.Front Physiol. 2018 Sep 10;9:1154. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01154. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30246797 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 24: Signal Transduction Pathways.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 27;15(13):3365. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133365. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444474 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Robb L. Cytokine receptors and hematopoietic differentiation. Oncogene. 2007;26:6715–6723. - PubMed
-
- Wormald S, Hilton D. Inhibitors of cytokine signal tranduction. J Biol Chem. 2003;279:821–824. - PubMed
-
- O’Sullivan LA, Liongue C, Lewis RS, Stephenson SEM, Ward AC. Cytokine receptor signaling through the Jak-Stat-Socs pathway in disease. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:2497–2506. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
