Comprehensive gene expression profiling reveals synergistic functional networks in cerebral vessels after hypertension or hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 23874591
- PMCID: PMC3712983
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068335
Comprehensive gene expression profiling reveals synergistic functional networks in cerebral vessels after hypertension or hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
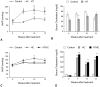
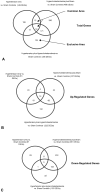
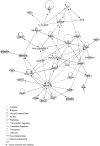
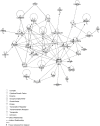
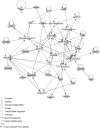
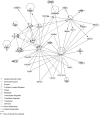
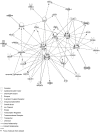
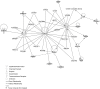
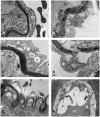
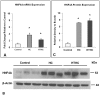
Atherosclerotic stenosis of cerebral arteries or intracranial large artery disease (ICLAD) is a major cause of stroke especially in Asians, Hispanics and Africans, but relatively little is known about gene expression changes in vessels at risk. This study compares comprehensive gene expression profiles in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) of New Zealand White rabbits exposed to two stroke risk factors i.e. hypertension and/or hypercholesterolemia, by the 2-Kidney-1-Clip method, or dietary supplementation with cholesterol. Microarray and Ingenuity Pathway Analyses of the MCA of the hypertensive rabbits showed up-regulated genes in networks containing the node molecules: UBC (ubiquitin), P38 MAPK, ERK, NFkB, SERPINB2, MMP1 and APP (amyloid precursor protein); and down-regulated genes related to MAPK, ERK 1/2, Akt, 26 s proteasome, histone H3 and UBC. The MCA of hypercholesterolemic rabbits showed differentially expressed genes that are surprisingly, linked to almost the same node molecules as the hypertensive rabbits, despite a relatively low percentage of 'common genes' (21 and 7%) between the two conditions. Up-regulated common genes were related to: UBC, SERPINB2, TNF, HNF4A (hepatocyte nuclear factor 4A) and APP, and down-regulated genes, related to UBC. Increased HNF4A message and protein were verified in the aorta. Together, these findings reveal similar nodal molecules and gene pathways in cerebral vessels affected by hypertension or hypercholesterolemia, which could be a basis for synergistic action of risk factors in the pathogenesis of ICLAD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures













Similar articles
-
Global gene expression changes in the prefrontal cortex of rabbits with hypercholesterolemia and/or hypertension.Neurochem Int. 2017 Jan;102:33-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.11.010. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Neurochem Int. 2017. PMID: 27890723
-
Cerebrovascular gene expression in spontaneously hypertensive rats.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 7;12(9):e0184233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184233. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28880918 Free PMC article.
-
Permeation and deposition of fibrinogen and low-density lipoprotein in the aorta and cerebral artery of rabbits--immuno-electron microscopic study.Br J Exp Pathol. 1984 Jun;65(3):355-64. Br J Exp Pathol. 1984. PMID: 6743533 Free PMC article.
-
Genes overexpressed in cerebral arteries following salt-induced hypertensive disease are regulated by angiotensin II, JunB, and CREB.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Feb;294(2):H1075-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00913.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18156195
-
Maternal hypercholesterolemia during pregnancy promotes early atherogenesis in LDL receptor-deficient mice and alters aortic gene expression determined by microarray.Circulation. 2002 Mar 19;105(11):1360-7. doi: 10.1161/hc1102.106792. Circulation. 2002. PMID: 11901049
Cited by
-
Deciphering the in vivo Dynamic Proteomics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Critical Limb Ischemia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 30;9:682476. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.682476. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34277623 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially Expressed Genes and Their Clinical Significance in Ischaemic Stroke: An In-Silico Study.Malays J Med Sci. 2020 Dec;27(6):53-67. doi: 10.21315/mjms2020.27.6.6. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Malays J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33447134 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic Exposure, Blood DNA Methylation, and Cardiovascular Disease.Circ Res. 2022 Jul 8;131(2):e51-e69. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.320991. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35658476 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression in Experimental Aortic Coarctation and Repair: Candidate Genes for Therapeutic Intervention?PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133356. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26207811 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Disease-Related Genes That Are Common between Alzheimer's and Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 23;9(11):1525. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111525. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong LK (2006) Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis. Int J Stroke 1: 158–159. - PubMed
-
- Gorelick PB, Wong KS, Bae HJ, Pandey DK (2008) Large artery intracranial occlusive disease: a large worldwide burden but a relatively neglected frontier. Stroke 39: 2396–2399. - PubMed
-
- Wong KS, Li H (2003) Long-term mortality and recurrent stroke risk among Chinese stroke patients with predominant intracranial atherosclerosis. Stroke 34: 2361–2366. - PubMed
-
- Mazighi M, Tanasescu R, Ducrocq X, Vicaut E, Bracard S, et al. (2006) Prospective study of symptomatic atherothrombotic intracranial stenoses: the GESICA study. Neurology 66: 1187–1191. - PubMed
-
- De Silva DA, Ancalan M, Doshi K, Chang HM, Wong MC, et al. (2009) Intracranial large artery disease in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia among ethnic Asians. Eur J Neurol 16: 643–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

