Drug-loaded sickle cells programmed ex vivo for delayed hemolysis target hypoxic tumor microvessels and augment tumor drug delivery
- PMID: 23871960
- PMCID: PMC4162096
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.07.008
Drug-loaded sickle cells programmed ex vivo for delayed hemolysis target hypoxic tumor microvessels and augment tumor drug delivery
Abstract
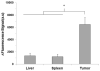
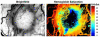
Selective drug delivery to hypoxic tumor niches remains a significant therapeutic challenge that calls for new conceptual approaches. Sickle red blood cells (SSRBCs) have shown an ability to target such hypoxic niches and induce tumoricidal effects when used together with exogenous pro-oxidants. Here we determine whether the delivery of a model therapeutic encapsulated in murine SSRBCs can be enhanced by ex vivo photosensitization under conditions that delay autohemolysis to a time that coincides with maximal localization of SSRBCs in a hypoxic tumor. Hyperspectral imaging of 4T1 carcinomas shows oxygen saturation levels <10% in a large fraction (commonly 50% or more) of the tumor. Using video microscopy of dorsal skin window chambers implanted with 4T1 tumors, we demonstrate that allogeneic SSRBCs, but not normal RBCs (nRBCs), selectively accumulate in hypoxic 4T1 tumors between 12 and 24h after systemic administration. We further show that ex vivo photo-oxidation can program SSRBCs to postpone hemolysis/release of a model therapeutic to a point that coincides with their maximum sequestration in hypoxic tumor microvessels. Under these conditions, drug-loaded photosensitized SSRBCs show a 3-4 fold greater drug delivery to tumors compared to non-photosensitized SSRBCs, drug-loaded photosensitized nRBCs, and free drug. These results demonstrate that photo-oxidized SSRBCs, but not photo-oxidized nRBCs, sequester and hemolyze in hypoxic tumors and release substantially more drug than photo-oxidized nRBCs and non-photo-oxidized SSRBCs. Photo-oxidation of drug-loaded SSRBCs thus appears to exploit the unique tumor targeting and carrier properties of SSRBCs to optimize drug delivery to hypoxic tumors. Such programmed and drug-loaded SSRBCs therefore represent a novel and useful tool for augmenting drug delivery to hypoxic solid tumors.
Keywords: Blood; Cancer; Carrier; Chemotherapy; Particle; Photosensitizer.
© 2013.
Figures
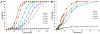
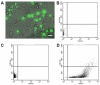
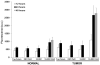
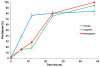
Comment in
-
Programmed sickle cells for targeted delivery to hypoxic tumors.J Control Release. 2013 Oct 28;171(2):258. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.08.027. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 24016418 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Sickle cells produce functional immune modulators and cytotoxics.Am J Hematol. 2017 Oct;92(10):981-988. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24836. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Am J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28646491 Free PMC article.
-
Sickle erythrocytes target cytotoxics to hypoxic tumor microvessels and potentiate a tumoricidal response.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e52543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052543. Epub 2013 Jan 9. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326340 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous sickle erythrocytes combined with vascular disruption trigger disseminated tumor vaso-occlusion and lung tumor regression.JCI Insight. 2019 Apr 4;4(7):e125535. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125535. eCollection 2019 Apr 4. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30944254 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of photosensitizing dyes for pathogen reduction in red cell suspensions.Biotech Histochem. 2003 Jun-Aug;78(3-4):171-7. doi: 10.1080/1052029032000140894. Biotech Histochem. 2003. PMID: 14714880 Review.
-
Tumor hypoxia: a target for selective cancer therapy.Cancer Sci. 2003 Dec;94(12):1021-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01395.x. Cancer Sci. 2003. PMID: 14662015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperspectral imaging of 4T1 mammary carcinomas grown in dorsal skinfold window chambers: spectral renormalization and fluorescence modeling.J Biomed Opt. 2024 Sep;29(9):093504. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.9.093504. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 39040986 Free PMC article.
-
A Macro Lens-Based Optical System Design for Phototherapeutic Instrumentation.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 9;19(24):5427. doi: 10.3390/s19245427. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31835391 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Emerging Clinical Applications of Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography (MSOT) in Oncology.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 15;22(14):3432-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0573. Epub 2016 May 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27208064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sickle cells produce functional immune modulators and cytotoxics.Am J Hematol. 2017 Oct;92(10):981-988. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24836. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Am J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28646491 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression Technique of HeLa Cell Proliferation Using Ultrasonic Power Amplifiers Integrated with a Series-Diode Linearizer.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Dec 3;18(12):4248. doi: 10.3390/s18124248. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30513959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain RK. Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001;46:149–168. - PubMed
-
- Terman D, Viglianti B, Zennadi R, Willmon C, Fels D, Boruta R, Yuan H, Dreher M, Grant G, Rabbani Z, Moon E, Lan L, Eble J, Cao Y, Sorg B, Ashcraft K, Palmer G, Telen M, Vile R, Dewhirst M. Sickle erythrocytes target cytotoxics/oncolytic virus to hypoxic tumor microvessels and potentiate a tumoricidal response. PLOS ONE. 2013;8:e52543. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Terman DS. Compositions and methods for treatment of neoplastic disease. 7,803,637 United States patent. 2010
-
- Ruoslahti E. Vascular zip codes in angiogenesis and metastasis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004;32:397–402. - PubMed
-
- Al-Akhras MA, Grossweiner LI. Sensitization of photohemolysis by hypericin and Photofrin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 1996;34:169–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

