Metabotropic glutamate receptors for Parkinson's disease therapy
- PMID: 23853735
- PMCID: PMC3703788
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/196028
Metabotropic glutamate receptors for Parkinson's disease therapy
Abstract
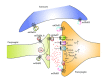
Excessive glutamatergic signalling within the basal ganglia is implicated in the progression of Parkinson's disease (PD) and inthe emergence of dyskinesia associated with long-term treatment with L-DOPA. There is considerable research focus on the discovery and development of compounds that modulate glutamatergic signalling via glutamate receptors, as treatments for PD and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (LID). Although initial preclinical studies with ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists showed antiparkinsonian and antidyskinetic activity, their clinical use was limited due to psychiatric adverse effects, with the exception of amantadine, a weak N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist, currently used to reduce dyskinesia in PD patients. Metabotropic receptor (mGlu receptor) modulators were considered to have a more favourable side-effect profile, and several agents have been studied in preclinical models of PD. The most promising results have been seen clinically with selective antagonists of mGlu5 receptor and preclinically with selective positive allosteric modulators of mGlu4 receptor. The growing understanding of glutamate receptor crosstalk also raises the possibility of more precise modulation of glutamatergic transmission, which may lead to the development of more effective agents for PD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors in Parkinson's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023;168:1-31. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36868628 Review.
-
mGlu5, Dopamine D2 and Adenosine A2A Receptors in L-DOPA-induced Dyskinesias.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(5):481-93. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666151201185652. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26639458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic treatment with MPEP, an mGlu5 receptor antagonist, normalizes basal ganglia glutamate neurotransmission in L-DOPA-treated parkinsonian monkeys.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Oct;73:216-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.028. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23756168
-
Glutamate modulation for the treatment of levodopa induced dyskinesia: a brief review of the drugs tested in the clinic.Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2022 Aug;12(4):203-214. doi: 10.2217/nmt-2021-0055. Epub 2022 May 19. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2022. PMID: 35587024 Review.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors as therapeutic targets in Parkinson's disease: An update from the last 5 years of research.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Mar 15;115:166-179. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.036. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27055772 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic activation of striatal cholinergic interneurons regulates L-dopa-induced dyskinesias.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Jul;91:47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.02.019. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 26921469 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis identifies risk factors in restless legs syndrome.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 20:2023.12.19.23300211. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.19.23300211. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Ann Neurol. 2024 Nov;96(5):994-1005. doi: 10.1002/ana.27040. PMID: 38168192 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A further update on the role of excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):849-59. doi: 10.1007/s00702-013-1149-z. Epub 2014 Jan 1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 24380931 Review.
-
Marijuana Compounds: A Nonconventional Approach to Parkinson's Disease Therapy.Parkinsons Dis. 2016;2016:1279042. doi: 10.1155/2016/1279042. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Parkinsons Dis. 2016. PMID: 28050308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDZ Scaffold Protein CAL Couples with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 to Protect Against Cell Apoptosis and Is a Potential Target in the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease.Neurotherapeutics. 2019 Jul;16(3):761-783. doi: 10.1007/s13311-019-00730-7. Neurotherapeutics. 2019. PMID: 31073978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mercuri NB, Bernardi G. The “magic” of L-dopa: why is it the gold standard Parkinson’s disease therapy? Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 2005;26(7):341–344. - PubMed
-
- Fabbrini G, Brotchie JM, Grandas F, Nomoto M, Goetz CG. Levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Movement Disorders. 2007;22(10):1379–1389. - PubMed
-
- Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Movement Disorders. 2001;16(3):448–458. - PubMed
-
- Cristina S, Zangaglia R, Mancini F, Martignoni E, Nappi G, Pacchetti C. High-dose ropinirole in advanced Parkinson’s disease with severe dyskinesias. Clinical Neuropharmacology. 2003;26(3):146–150. - PubMed
-
- Facca A, Sanchez-Ramos J. High-dose pergolide monotherapy in the treatment of severe levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Movement Disorders. 1996;11(3):327–329. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

