The neuronal transcription factor erect wing regulates specification and maintenance of Drosophila R8 photoreceptor subtypes
- PMID: 23850772
- PMCID: PMC3757101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.07.001
The neuronal transcription factor erect wing regulates specification and maintenance of Drosophila R8 photoreceptor subtypes
Abstract
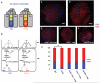
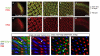
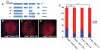
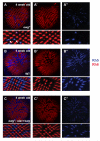
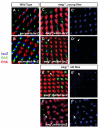
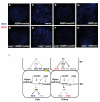
Signaling pathways are often re-used during development in surprisingly different ways. The Hippo tumor suppressor pathway is best understood for its role in the control of growth. The pathway is also used in a very different context, in the Drosophila eye for the robust specification of R8 photoreceptor neuron subtypes, which complete their terminal differentiation by expressing light-sensing Rhodopsin (Rh) proteins. A double negative feedback loop between the Warts kinase of the Hippo pathway and the PH-domain growth regulator Melted regulates the choice between 'pale' R8 (pR8) fate defined by Rh5 expression and 'yellow' R8 (yR8) fate characterized by Rh6 expression. Here, we show that the gene encoding the homolog of human Nuclear respiratory factor 1, erect wing (ewg), is autonomously required to inhibit warts expression and to promote melted expression to specify pR8 subtype fate and induce Rh5. ewg mutants express Rh6 in most R8s due to ectopic warts expression. Further, ewg is continuously required to maintain repression of Rh6 in pR8s in aging flies. Our work shows that Ewg is a critical factor for the stable down-regulation of Hippo pathway activity to determine neuronal subtype fates. Neural-enriched factors, such as Ewg, may generally contribute to the contextual re-use of signaling pathways in post-mitotic neurons.
Keywords: Drosophila; Ewg; Hippo pathway; Photoreceptors; R8; Retina; Rhodopsin.
© 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The insulator protein BEAF-32 is required for Hippo pathway activity in the terminal differentiation of neuronal subtypes.Development. 2016 Jul 1;143(13):2389-97. doi: 10.1242/dev.134700. Epub 2016 May 25. Development. 2016. PMID: 27226322 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing transcriptional and post-transcriptional roles for Scalloped in binary Hippo-dependent neural fate decisions.Dev Biol. 2019 Nov 1;455(1):51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.06.022. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31265830 Free PMC article.
-
Binary regulation of Hippo pathway by Merlin/NF2, Kibra, Lgl, and Melted specifies and maintains postmitotic neuronal fate.Dev Cell. 2011 Nov 15;21(5):874-87. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.10.004. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 22055343 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons about terminal differentiation from the specification of color-detecting photoreceptors in the Drosophila retina.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013 Jul;1293:33-44. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12178. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013. PMID: 23782311 Review.
-
Eye development: stable cell fate decisions in insect colour vision.Curr Biol. 2005 Nov 22;15(22):R924-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.10.062. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16303550 Review.
Cited by
-
The insulator protein BEAF-32 is required for Hippo pathway activity in the terminal differentiation of neuronal subtypes.Development. 2016 Jul 1;143(13):2389-97. doi: 10.1242/dev.134700. Epub 2016 May 25. Development. 2016. PMID: 27226322 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study and transcriptome analysis reveals a complex gene network that regulates opsin gene expression and cell fate determination in Drosophila R7 photoreceptor cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 7:2024.08.05.606616. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.05.606616. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149333 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Essential roles of mitochondrial biogenesis regulator Nrf1 in retinal development and homeostasis.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Oct 17;13(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0287-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30333037 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in four glycosyl hydrolases reveal a highly coordinated pathway for rhodopsin biosynthesis and N-glycan trimming in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2014 May 1;10(5):e1004349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004349. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24785692 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel Activin and BMP signaling coordinates R7/R8 photoreceptor subtype pairing in the stochastic Drosophila retina.Elife. 2017 Aug 30;6:e25301. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25301. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28853393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrio R, de Celis JF, Bolshakov S, Kafatos FC. Identification of regulatory regions driving the expression of the Drosophila spalt complex at different developmental stages. Developmental biology. 1999;215:33–47. - PubMed
-
- Calzone FJ, Hoog C, Teplow DB, Cutting AE, Zeller RW, Britten RJ, Davidson EH. Gene regulatory factors of the sea urchin embryo. I. Purification by affinity chromatography and cloning of P3A2, a novel DNA-binding protein. Development. 1991;112:335–350. - PubMed
-
- Chou WH, Hall KJ, Wilson DB, Wideman CL, Townson SM, Chadwell LV, Britt SG. Identification of a novel Drosophila opsin reveals specific patterning of the R7 and R8 photoreceptor cells. Neuron. 1996;17:1101–1115. - PubMed
-
- Chou WH, Huber A, Bentrop J, Schulz S, Schwab K, Chadwell LV, Paulsen R, Britt SG. Patterning of the R7 and R8 photoreceptor cells of Drosophila: evidence for induced and default cell-fate specification. Development. 1999;126:607–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

