Put a RING on it: regulation and inhibition of RNF8 and RNF168 RING finger E3 ligases at DNA damage sites
- PMID: 23847653
- PMCID: PMC3705210
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00128
Put a RING on it: regulation and inhibition of RNF8 and RNF168 RING finger E3 ligases at DNA damage sites
Abstract
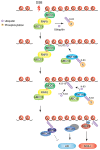
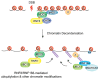
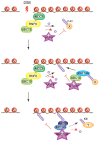
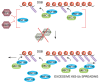
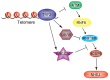
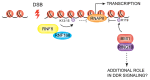
RING (Really Interesting New Gene) domain-containing E3 ubiquitin ligases comprise a large family of enzymes that in combination with an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, modify target proteins by attaching ubiquitin moieties. A number of RING E3s play an essential role in the cellular response to DNA damage highlighting a crucial contribution for ubiquitin-mediated signaling to the genome surveillance pathway. Among the RING E3s, RNF8 and RNF168 play a critical role in the response to double stranded breaks, one of the most deleterious types of DNA damage. These proteins act as positive regulators of the signaling cascade that initiates at DNA lesions. Inactivation of these enzymes is sufficient to severely impair the ability of cells to respond to DNA damage. Given their central role in the pathway, several layers of regulation act at this nodal signaling point. Here we will summarize current knowledge on the roles of RNF8 and RNF168 in maintaining genome integrity with particular emphasis on recent insights into the multiple layers of regulation that act on these enzymes to fine-tune the cellular response to DNA lesions.
Keywords: DNA damage response; HR; NHEJ; RING E3 ligase; RNF168; RNF8; genomic stability; ubiquitin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for role of ring finger protein RNF168 RING domain.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 15;12(2):312-21. doi: 10.4161/cc.23104. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23255131 Free PMC article.
-
RNF8 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Stimulates Ubc13 E2 Conjugating Activity That Is Essential for DNA Double Strand Break Signaling and BRCA1 Tumor Suppressor Recruitment.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9396-410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.715698. Epub 2016 Feb 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26903517 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 22;19(2):201-6. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2211. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22266820 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles of RNF8/RNF168 and deubiquitinating enzymes in ubiquitination-dependent DNA double-strand break response signaling and DNA-repair pathway choice.J Radiat Res. 2016 Aug;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i33-i40. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw027. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 26983989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of RNF168 in Tumor Progression.Molecules. 2023 Feb 2;28(3):1417. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031417. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771081 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNF8-CDH1 Co-Expression Predicts Clinical Benefit of Chemoradiotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.J Pers Med. 2021 Jul 13;11(7):655. doi: 10.3390/jpm11070655. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34357122 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitylation of Rad51d Mediated by E3 Ligase Rnf138 Promotes the Homologous Recombination Repair Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 May 19;11(5):e0155476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155476. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27195665 Free PMC article.
-
LC8/DYNLL1 is a 53BP1 effector and regulates checkpoint activation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6236-6249. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz263. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30982887 Free PMC article.
-
A fine-scale dissection of the DNA double-strand break repair machinery and its implications for breast cancer therapy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):6106-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku284. Epub 2014 May 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24792170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 regulates nucleotide excision repair through deubiquitinating XPC protein and preventing XPC protein from undergoing ultraviolet light-induced and VCP/p97 protein-regulated proteolysis.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 26;289(39):27278-27289. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589812. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25118285 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

