An M2e-based synthetic peptide vaccine for influenza A virus confers heterosubtypic protection from lethal virus challenge
- PMID: 23834899
- PMCID: PMC3716895
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-227
An M2e-based synthetic peptide vaccine for influenza A virus confers heterosubtypic protection from lethal virus challenge
Abstract
Background: Vaccination is considered as the most effective preventive method to control influenza. The hallmark of influenza virus is the remarkable variability of its major surface glycoproteins, HA and NA, which allows the virus to evade existing anti-influenza immunity in the target population. So it is necessary to develop a novel vaccine to control animal influenza virus. Also we know that the ectodomain of influenza matrix protein 2 (M2e) is highly conserved in animal influenza A viruses, so a vaccine based on the M2e could avoid several drawbacks of the traditional vaccines. In this study we designed a novel tetra-branched multiple antigenic peptide (MAP) based vaccine, which was constructed by fusing four copies of M2e to one copy of foreign T helper (Th) cell epitope, and then investigated its immune responses.
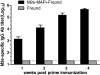
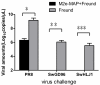
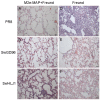
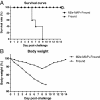
Results: Our results show that the M2e-MAP induced strong M2e-specific IgG antibody,which responses following 2 doses immunization in the presence of Freunds' adjuvant. M2e-MAP vaccination limited viral replication substantially. Also it could attenuate histopathological damage in the lungs of challenged mice and counteracted weight loss. M2e-MAP-based vaccine protected immunized mice against the lethal challenge with PR8 virus.
Conclusions: Based on these findings, M2e-MAP-based vaccine seemed to provide useful information for the research of M2e-based influenza vaccine. Also it show huge potential to study vaccines for other similarly viruses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An M2e-based multiple antigenic peptide vaccine protects mice from lethal challenge with divergent H5N1 influenza viruses.Virol J. 2010 Jan 18;7:9. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-9. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20082709 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal adenovirus-vectored vaccine for induction of long-lasting humoral immunity-mediated broad protection against influenza in mice.J Virol. 2014 Sep 1;88(17):9693-703. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00823-14. Epub 2014 Jun 11. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24920793 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a candidate influenza vaccine based on virus-like particles displaying influenza M2e peptide into the immunodominant region of hepatitis B core antigen: Broad protective efficacy of particles carrying four copies of M2e.Vaccine. 2015 Jun 26;33(29):3398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.04.073. Epub 2015 May 11. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25976545
-
M2e-Based Influenza Vaccines with Nucleoprotein: A Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jul 4;9(7):739. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9070739. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34358155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards a universal influenza vaccine: volunteer virus challenge studies in quarantine to speed the development and subsequent licensing.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;76(2):210-6. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12146. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23617282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA vaccine based on conserved HA-peptides induces strong immune response and rapidly clears influenza virus infection from vaccinated pigs.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 25;14(9):e0222201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222201. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31553755 Free PMC article.
-
Efforts to Improve the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine.Vaccines (Basel). 2018 Mar 30;6(2):19. doi: 10.3390/vaccines6020019. Vaccines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29601497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Universal influenza vaccines, a dream to be realized soon.Viruses. 2014 Apr 29;6(5):1974-91. doi: 10.3390/v6051974. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 24784572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Protective Immunity of Peptide Vaccines Composed of a 15-mer N-terminal Matrix Protein 2 and a Helper T-Cell Epitope Derived from Influenza A Virus.Immune Netw. 2019 Jul 23;19(4):e29. doi: 10.4110/in.2019.19.e29. eCollection 2019 Aug. Immune Netw. 2019. PMID: 31501717 Free PMC article.
-
The Unexpected Impact of Vaccines on Secondary Bacterial Infections Following Influenza.Viral Immunol. 2018 Mar;31(2):159-173. doi: 10.1089/vim.2017.0138. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Viral Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29148920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cox RJ, Brokstad KA, Ogra P. Influenza Virus: Immunity and Vaccination Strategies. Comparison of the Immune Response to Inactivated and Live, Attenuated Influenza Vaccines. Scand J Immunol. 2004;10:1365–3083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

