Design, synthesis, and optimization of novel epoxide incorporating peptidomimetics as selective calpain inhibitors
- PMID: 23834438
- PMCID: PMC3962784
- DOI: 10.1021/jm4006719
Design, synthesis, and optimization of novel epoxide incorporating peptidomimetics as selective calpain inhibitors
Abstract
Hyperactivation of the calcium-dependent cysteine protease calpain 1 (Cal1) is implicated as a primary or secondary pathological event in a wide range of illnesses and in neurodegenerative states, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). E-64 is an epoxide-containing natural product identified as a potent nonselective, calpain inhibitor, with demonstrated efficacy in animal models of AD. By use of E-64 as a lead, three successive generations of calpain inhibitors were developed using computationally assisted design to increase selectivity for Cal1. First generation analogues were potent inhibitors, effecting covalent modification of recombinant Cal1 catalytic domain (Cal1cat), demonstrated using LC-MS/MS. Refinement yielded second generation inhibitors with improved selectivity. Further library expansion and ligand refinement gave three Cal1 inhibitors, one of which was designed as an activity-based protein profiling probe. These were determined to be irreversible and selective inhibitors by kinetics studies comparing full length Cal1 with the general cysteine protease papain.
Figures

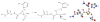


Similar articles
-
Green asymmetric synthesis of epoxypeptidomimetics and evaluation as human cathepsin K inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Aug 1;28(15):115597. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115597. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32631567
-
Rational Design of Calpain Inhibitors Based on Calpastatin Peptidomimetics.J Med Chem. 2016 Jun 9;59(11):5403-15. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00267. Epub 2016 May 18. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27148623
-
Crystal structures of calpain-E64 and -leupeptin inhibitor complexes reveal mobile loops gating the active site.J Mol Biol. 2004 Nov 5;343(5):1313-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.016. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15491615
-
An updated patent review of calpain inhibitors (2012 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Jan;25(1):17-31. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.982534. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015. PMID: 25399719 Review.
-
Calpain inhibitors: a survey of compounds reported in the patent and scientific literature.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011 May;21(5):601-36. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2011.568480. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011. PMID: 21434837 Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic therapy in Alzheimer's disease: a CREB-centric approach.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Jan;12(1):29-41. doi: 10.1007/s13311-014-0327-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 25575647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteine proteases as therapeutic targets: does selectivity matter? A systematic review of calpain and cathepsin inhibitors.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Nov;5(6):506-19. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26713267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epoxide based inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus non-structural 2 autoprotease.Antiviral Res. 2015 May;117:20-6. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 25703928 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Tethering of Fragments For Covalent Probe Discovery.Medchemcomm. 2016 Apr 1;7(4):576-585. doi: 10.1039/c5md00518c. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Medchemcomm. 2016. PMID: 27398190 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating the Metabolic Liability of Carbonyl Reduction: Novel Calpain Inhibitors with P1' Extension.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018 Feb 4;9(3):221-226. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00494. eCollection 2018 Mar 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 29541364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei WEI, Cong J. The Calpain System. Phys. Rev. 2003;83:731–801. - PubMed
-
- Perlmutter LS, Siman R, Gall C, Seubert P, Baudry M, Lynch G. The ultrastructural localization of calcium-activated protease "calpain" in rat brain. Synapse. 1988;2:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Veeranna, Kaji T, Boland B, Odrljin T, Mohan P, Basavarajappa BS, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A, Rudnicki A, Amin N, Li BS, Pant HC, Hungund BL, Arancio O, Nixon RA. Calpain mediates calcium-induced activation of the erk1,2 MAPK pathway and cytoskeletal phosphorylation in neurons: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2004;165:795–805. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shea TB. Restriction of microM-calcium-requiring calpain activation to the plasma membrane in human neuroblastoma cells: evidence for regionalized influence of a calpain activator protein. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997;48:543–550. - PubMed
-
- Di Rosa G, Odrijin T, Nixon RA, Arancio O. Calpain inhibitors: a treatment for Alzheimer's disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2002;19:135–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

