A conditional zebrafish MITF mutation reveals MITF levels are critical for melanoma promotion vs. regression in vivo
- PMID: 23831555
- PMCID: PMC3898314
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2013.293
A conditional zebrafish MITF mutation reveals MITF levels are critical for melanoma promotion vs. regression in vivo
Abstract
The microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is the "master melanocyte transcription factor" with a complex role in melanoma. MITF protein levels vary between and within clinical specimens, and amplifications and gain- and loss-of-function mutations have been identified in melanoma. How MITF functions in melanoma development and the effects of targeting MITF in vivo are unknown because MITF levels have not been directly tested in a genetic animal model. Here, we use a temperature-sensitive mitf zebrafish mutant to conditionally control endogenous MITF activity. We show that low levels of endogenous MITF activity are oncogenic with BRAF(V600E) to promote melanoma that reflects the pathology of the human disease. Remarkably, abrogating MITF activity in BRAF(V600E)mitf melanoma leads to dramatic tumor regression marked by melanophage infiltration and increased apoptosis. These studies are significant because they show that targeting MITF activity is a potent antitumor mechanism, but also show that caution is required because low levels of wild-type MITF activity are oncogenic.
Figures
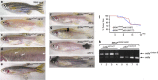
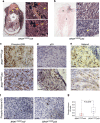

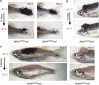
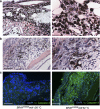
Comment in
-
Fishful thinking: the rise and fall of MITF in melanoma.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014 Jan;27(1):7-8. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12177. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014. PMID: 24118901 No abstract available.
-
The impact of MITF on melanoma development: news from bench and bedside.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jan;134(1):16-17. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.390. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24352080 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Deciphering the Role of Oncogenic MITFE318K in Senescence Delay and Melanoma Progression.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017 Aug 1;109(8). doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw340. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017. PMID: 28376192
-
Inhibition of oncogenic BRAF activity by indole-3-carbinol disrupts microphthalmia-associated transcription factor expression and arrests melanoma cell proliferation.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Jan;56(1):49-61. doi: 10.1002/mc.22472. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 26878440 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of MITF on melanoma development: news from bench and bedside.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Jan;134(1):16-17. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.390. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24352080 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and pigmentation in melanoma.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Dec 1;563:28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.07.019. Epub 2014 Aug 9. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 25111671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A germline oncogenic MITF mutation and tumor susceptibility.Eur J Cell Biol. 2014 Jan-Feb;93(1-2):71-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 26. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24290354 Review.
Cited by
-
The melanocyte lineage in development and disease.Development. 2015 Feb 15;142(4):620-32. doi: 10.1242/dev.106567. Development. 2015. PMID: 25670789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feeding amount significantly alters overt tumor onset rate in a zebrafish melanoma model.Biol Open. 2018 Jan 23;7(1):bio030726. doi: 10.1242/bio.030726. Biol Open. 2018. PMID: 29362277 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic melanoma cell death mediated by inhibition of both MCL1 and BCL2 in high-risk tumors driven by NF1/PTEN loss.Oncogene. 2021 Sep;40(38):5718-5729. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01926-y. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34331013 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocyte lineage dynamics in development, growth and disease.Development. 2024 Aug 1;151(15):dev201266. doi: 10.1242/dev.201266. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Development. 2024. PMID: 39092608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish Models of Cancer-New Insights on Modeling Human Cancer in a Non-Mammalian Vertebrate.Genes (Basel). 2019 Nov 15;10(11):935. doi: 10.3390/genes10110935. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31731811 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bertolotto C, Lesueur F, Giuliano S, et al. A SUMOylation-defective MITF germline mutation predisposes to melanoma and renal carcinoma. Nature. 2011;480:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Beuret L, Flori E, Denoyelle C, et al. Up-regulation of MET expression by alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and MITF allows hepatocyte growth factor to protect melanocytes and melanoma cells from apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14140–14147. - PubMed
-
- Cheli Y, Giuliano S, Fenouille N, et al. Hypoxia and MITF control metastatic behaviour in mouse and human melanoma cells. Oncogene. 2012;10:2461–2470. - PubMed
-
- Cheli Y, Giuliano S, Botton T, et al. Mitf is the key molecular switch between mouse or human melanoma initiating cells and their differentiated progeny. Oncogene. 2011;30:2307–2318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

