FGF14 regulates presynaptic Ca2+ channels and synaptic transmission
- PMID: 23831029
- PMCID: PMC3736584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.012
FGF14 regulates presynaptic Ca2+ channels and synaptic transmission
Abstract
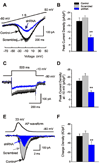
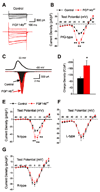
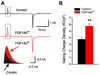
Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors (FHFs) are not growth factors, but instead bind to voltage-gated Na+ channels (NaV) and regulate their function. Mutations in FGF14, an FHF that is the locus for spinocerebellar ataxia 27 (SCA27), are believed to be pathogenic because of a dominant-negative reduction of NaV currents in cerebellar granule cells. Here, we demonstrate that FGF14 also regulates members of the presynaptic CaV2 Ca2+ channel family. Knockdown of FGF14 in granule cells reduced Ca2+ currents and diminished vesicular recycling, a marker for presynaptic Ca2+ influx. As a consequence, excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) at the granule cell to Purkinje cell synapse were markedly diminished. Expression of the SCA27-causing FGF14 mutant in granule cells exerted a dominant-negative reduction in Ca2+ currents, vesicular recycling, and the resultant EPSCs in Purkinje cells. Thus, FHFs are multimodal, regulating several discrete neuronal signaling events. SCA27 most likely results at least in part from dysregulation of Ca2+ channel function.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
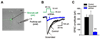
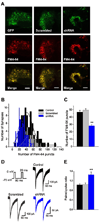
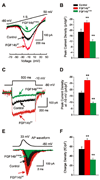
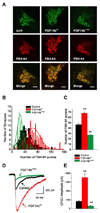
Similar articles
-
Intracellular FGF14 (iFGF14) Is Required for Spontaneous and Evoked Firing in Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons and for Motor Coordination and Balance.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 29;35(17):6752-69. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2663-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25926453 Free PMC article.
-
FGF14 regulates the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar Purkinje neurons.Neurobiol Dis. 2009 Jan;33(1):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.09.019. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Neurobiol Dis. 2009. PMID: 18930825 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synaptic impairment in a mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxia type 27.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jun 4;9:205. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00205. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26089778 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrin II expressing Purkinje cell phenotype-related and -unrelated cerebellar abnormalities in Cav2.1 mutant, rolling mouse Nagoya.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Oct 12;10:2032-8. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.205. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20953553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic Calcium Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 6;20(9):2217. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092217. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31064106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular FGF14 (iFGF14) Is Required for Spontaneous and Evoked Firing in Cerebellar Purkinje Neurons and for Motor Coordination and Balance.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 29;35(17):6752-69. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2663-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25926453 Free PMC article.
-
FGF14 modulates resurgent sodium current in mouse cerebellar Purkinje neurons.Elife. 2014 Sep 30;3:e04193. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04193. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25269146 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomics reveals protein-protein interactions with fibroblast growth factor 12 as a component of the voltage-gated sodium channel 1.2 (nav1.2) macromolecular complex in Mammalian brain.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 May;14(5):1288-300. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.040055. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25724910 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Tuning of the Axonal Mitochondrial Ca2+ Uniporter Ensures Metabolic Flexibility of Neurotransmission.Neuron. 2020 Feb 19;105(4):678-687.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.020. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 31862210 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of Fgf14 in behavioral control.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 1;356:257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.034. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30189289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister RA, Melliti K, Adams BA. Differential modulation of CaV2.3 Ca2+ channels by Galphaq/11-coupled muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;65:381–388. - PubMed
-
- Dalski A, Atici J, Kreuz FR, Hellenbroich Y, Schwinger E, Zuhlke C. Mutation analysis in the fibroblast growth factor 14 gene: frameshift mutation and polymorphisms in patients with inherited ataxias. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005;13:118–120. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher CF, Lutz CM, O'Sullivan TN, Shaughnessy JD, Jr., Hawkes R, Frankel WN, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. Absence epilepsy in tottering mutant mice is associated with calcium channel defects. Cell. 1996;87:607–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

