IMDB network revisited: unveiling fractal and modular properties from a typical small-world network
- PMID: 23826098
- PMCID: PMC3691214
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066443
IMDB network revisited: unveiling fractal and modular properties from a typical small-world network
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(8). doi:10.1371/annotation/7ce29312-158e-49b2-b530-6aca07751cea
Abstract
We study a subset of the movie collaboration network, http://www.imdb.com, where only adult movies are included. We show that there are many benefits in using such a network, which can serve as a prototype for studying social interactions. We find that the strength of links, i.e., how many times two actors have collaborated with each other, is an important factor that can significantly influence the network topology. We see that when we link all actors in the same movie with each other, the network becomes small-world, lacking a proper modular structure. On the other hand, by imposing a threshold on the minimum number of links two actors should have to be in our studied subset, the network topology becomes naturally fractal. This occurs due to a large number of meaningless links, namely, links connecting actors that did not actually interact. We focus our analysis on the fractal and modular properties of this resulting network, and show that the renormalization group analysis can characterize the self-similar structure of these networks.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
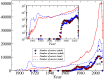
 of actors participated in a movie (as reported in IMDB). b) Distribution of the links weights, or equivalently, the probability that two actors have participated in
of actors participated in a movie (as reported in IMDB). b) Distribution of the links weights, or equivalently, the probability that two actors have participated in  movies together.
movies together.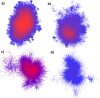
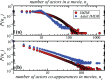
 , 14444, 5315, and 2100 actors, respectively.
, 14444, 5315, and 2100 actors, respectively.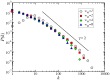
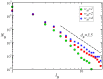
 (see text).
(see text).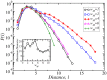
 .
.
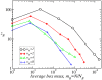
 , the other networks have a fractal dimension, shown by the dashed line with slope,
, the other networks have a fractal dimension, shown by the dashed line with slope,  .
.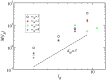
 , with a slope close to
, with a slope close to  , as shown by the dashed line with the same slope value.
, as shown by the dashed line with the same slope value.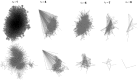
 . Bottom row: Adult IMDB network at
. Bottom row: Adult IMDB network at  .
.
Similar articles
-
Box-covering algorithm for fractal dimension of complex networks.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2012 Jul;86(1 Pt 2):016707. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.86.016707. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2012. PMID: 23005563
-
Fractal rules in brain networks: Signatures of self-organization.J Theor Biol. 2018 Jan 21;437:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.09.014. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Theor Biol. 2018. PMID: 28935234
-
Scaling in topological properties of brain networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 26;6:24926. doi: 10.1038/srep24926. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27112129 Free PMC article.
-
Health, 'small-worlds', fractals and complex networks: an emerging field.Med Sci Monit. 2003 May;9(5):MT19-23. Med Sci Monit. 2003. PMID: 12761464 Review.
-
The fractal architecture of cytoplasmic organization: scaling, kinetics and emergence in metabolic networks.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 Jan-Feb;256-257(1-2):169-84. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000009867.54552.09. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 14977179 Review.
Cited by
-
Popcorn in the pain clinic: A content analysis of the depiction of patients with chronic pain and their management in motion pictures.Can J Pain. 2022 Oct 27;6(1):195-210. doi: 10.1080/24740527.2022.2123308. eCollection 2022. Can J Pain. 2022. PMID: 36324369 Free PMC article.
-
"Give My Daughter the Shot!": A Content Analysis of the Depiction of Patients with Cancer Pain and Their Management in Hollywood Films.Curr Oncol. 2022 Oct 29;29(11):8207-8221. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29110648. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36354708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scaling theory of fractal complex networks.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 20;14(1):9079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59765-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38643243 Free PMC article.
-
Lights, camera, scalpel: a lookback at 100 years of plastic surgery on the silver screen.Eur J Plast Surg. 2021;44(5):551-561. doi: 10.1007/s00238-021-01834-0. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Eur J Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34253940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collaboration networks from a large CV database: dynamics, topology and bonus impact.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 6;9(3):e90537. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090537. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24603470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert R, Barabási AL (2002) Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys 74: 47–97.
-
- Boccaletti S, Latora V, Moreno Y, Chavez M, Hwang DU (2006) Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Physics Reports 424: 175–308.
-
- Fararo T, Sunshine MH (1964) A Study of a Biased Friendship Net. Syracuse, NY, USA: Syracuse University Press.
-
- Bernard HR, Killworth DD, Evans MJ, McCarty C, Shelley GA (1988) Studying social-relations cross-culturally. Ethnology 27: 155–179.
-
- Vanraan AFJ (1990) Fractal dimension of co-citations. Nature 347: 626.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

