Negative regulation of TLR inflammatory signaling by the SUMO-deconjugating enzyme SENP6
- PMID: 23825957
- PMCID: PMC3694847
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003480
Negative regulation of TLR inflammatory signaling by the SUMO-deconjugating enzyme SENP6
Abstract
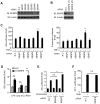
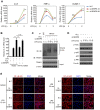
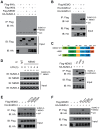
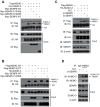
The signaling of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) induces host defense against microbial invasion. Protein posttranslational modifications dynamically shape the strength and duration of the signaling pathways. It is intriguing to explore whether de-SUMOylation could modulate the TLR signaling. Here we identified SUMO-specific protease 6 (SENP6) as an intrinsic attenuator of the TLR-triggered inflammation. Depletion of SENP6 significantly potentiated the NF-κB-mediated induction of the proinflammatory genes. Consistently, SENP6-knockdown mice were more susceptible to endotoxin-induced sepsis. Mechanistically, the small ubiquitin-like modifier 2/3 (SUMO-2/3) is conjugated onto the Lysine residue 277 of NF-κB essential modifier (NEMO/IKKγ), and this impairs the deubiquitinase CYLD to bind NEMO, thus strengthening the inhibitor of κB kinase (IKK) activation. SENP6 reverses this process by catalyzing the de-SUMOylation of NEMO. Our study highlights the essential function of the SENP family in dampening TLR signaling and inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Swapping small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) isoform specificity of SUMO proteases SENP6 and SENP7.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 14;286(41):36142-36151. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.268847. Epub 2011 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21878624 Free PMC article.
-
The poly-SUMO2/3 protease SENP6 enables assembly of the constitutive centromere-associated network by group deSUMOylation.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 4;10(1):3987. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11773-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31485003 Free PMC article.
-
SENP1-mediated NEMO de-SUMOylation inhibits intermittent hypoxia induced inflammatory response of microglia in vitro.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Apr;235(4):3529-3538. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29241. Epub 2019 Sep 24. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31549402
-
The fate of metaphase kinetochores is weighed in the balance of SUMOylation during S phase.Cell Cycle. 2010 Aug 15;9(16):3194-201. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.16.12619. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20724819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-protein interactions involving IKKgamma (NEMO) that promote the activation of NF-kappaB.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jun;223(3):558-61. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22105. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20301198 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring potential targets for natural product therapy of DN: the role of SUMOylation.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 4;15:1432724. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1432724. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39431155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial sensing by Toll-like receptors and intracellular nucleic acid sensors.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 9;7(1):a016246. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016246. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25301932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Desumoylase SENP6 maintains osteochondroprogenitor homeostasis by suppressing the p53 pathway.Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 10;9(1):143. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02413-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29321472 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine attenuates LPS-mediated macrophage activation through miR-669n-regulated SENP6 protein translation.Am J Transl Res. 2015 Nov 15;7(11):2335-45. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26807181 Free PMC article.
-
Fast friends - Ubiquitin-like modifiers as engineered fusion partners.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec;132:132-145. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.11.013. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34840080 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11: 373–384. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R (2007) Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 449: 819–826. - PubMed
-
- Cook DN, Pisetsky DS, Schwartz DA (2004) Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of human disease. Nat Immunol 5: 975–979. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B (2004) Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 430: 257–263. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 499–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

