Desensitization of human CRF2(a) receptor signaling governed by agonist potency and βarrestin2 recruitment
- PMID: 23820308
- PMCID: PMC3924877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2013.06.009
Desensitization of human CRF2(a) receptor signaling governed by agonist potency and βarrestin2 recruitment
Abstract
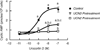
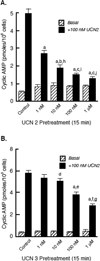
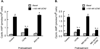
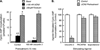
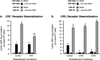
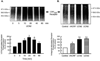
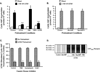
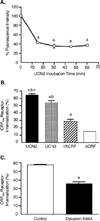
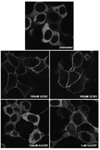
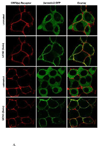
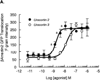
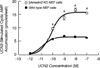
The primary goal was to determine agonist-specific regulation of CRF2(a) receptor function. Exposure of human retinoblastoma Y79 cells to selective (UCN2, UCN3 or stresscopins) and non-selective (UCN1 or sauvagine) agonists prominently desensitized CRF2(a) receptors in a rapid, concentration-dependent manner. A considerably slower rate and smaller magnitude of desensitization developed in response to the weak agonist CRF. CRF1 receptor desensitization stimulated by CRF, cortagine or stressin1-A had no effect on CRF2(a) receptor cyclic AMP signaling. Conversely, desensitization of CRF2(a) receptors by UCN2 or UCN3 did not cross-desensitize Gs-coupled CRF1 receptor signaling. In transfected HEK293 cells, activation of CRF2(a) receptors by UCN2, UCN3 or CRF resulted in receptor phosphorylation and internalization proportional to agonist potency. Neither protein kinase A nor casein kinases mediated CRF2(a) receptor phosphorylation or desensitization. Exposure of HEK293 or U2OS cells to UCN2 or UCN3 (100nM) produced strong βarrestin2 translocation and colocalization with membrane CRF2(a) receptors while CRF (1μM) generated only weak βarrestin2 recruitment. βarrestin2 did not internalize with the receptor, however, indicating that transient CRF2(a) receptor-arrestin complexes dissociate at or near the cell membrane. Since deletion of the βarrestin2 gene upregulated Gs-coupled CRF2(a) receptor signaling in MEF cells, a βarrestin2 mechanism restrains Gs-coupled CRF2(a) receptor signaling activated by urocortins. We further conclude that the rate and extent of homologous CRF2(a) receptor desensitization are governed by agonist-specific mechanisms affecting GRK phosphorylation, βarrestin2 recruitment, and internalization thereby producing unique signal transduction profiles that differentially affect the stress response.
Keywords: CK1; CK2; CRF receptor type 1; CRF receptor type 2(a); CRF(1) receptor; CRF(2(a)) receptor; Corticotropin releasing factor receptor (CRF); G protein-coupled receptor; GPCR; GPCR kinase; GRK; K44A; PKA; PKC; SCP; SRP; Urocortin 1 (UCN1); Urocortin 2 (UCN2); Urocortin 3 (UCN3); casein kinase 1; casein kinase 2; dynamin dominant negative mutant; protein kinase A; protein kinase C; stresscopin; stresscopin-related peptide; βarrestin2.
© 2013.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of CRF and the urocortins on the hippocampal acetylcholine release in rats.Neuropeptides. 2021 Aug;88:102147. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2021.102147. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Neuropeptides. 2021. PMID: 33932861
-
Agonist bias and agonist-dependent antagonism at corticotrophin releasing factor receptors.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020 Jun;8(3):e00595. doi: 10.1002/prp2.595. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32529807 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, binding, and signaling properties of CRF2(a) receptors endogenously expressed in human retinoblastoma Y79 cells: passage-dependent regulation of functional receptors.J Neurochem. 2008 Feb;104(4):926-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05052.x. Epub 2007 Nov 1. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 17976162 Free PMC article.
-
The peripheral corticotropin releasing factor family's role in vasculitis.Vascul Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;154:107275. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107275. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Vascul Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38184094 Review.
-
The suppression effects of feeding and mechanisms in CRF system of animals.Gene. 2020 Apr 5;733:144363. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144363. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31935510 Review.
Cited by
-
Xiao Yao San Improves Depressive-Like Behavior in Rats through Modulation of β-Arrestin 2-Mediated Pathways in Hippocampus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:902516. doi: 10.1155/2014/902516. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 25097660 Free PMC article.
-
The CRF System as a Therapeutic Target for Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Dec;37(12):1045-1054. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27717506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor Type 2 Agonism Results in Sustained Symptom Improvement in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.Front Syst Neurosci. 2021 Sep 1;15:698240. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2021.698240. eCollection 2021. Front Syst Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34539356 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral CRF-R1/CRF-R2 antagonist, astressin C, induces a long-lasting blockade of acute stress-related visceral pain in male and female rats.Peptides. 2022 Nov;157:170881. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170881. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Peptides. 2022. PMID: 36185037 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrinology and the brain: corticotropin-releasing hormone signaling.Endocr Connect. 2017 Aug;6(6):R99-R120. doi: 10.1530/EC-17-0111. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Endocr Connect. 2017. PMID: 28710078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perrin MH, Vale W. Chapter 25: Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors. In: Pangalos MN, Davies CH, editors. Understanding G protein-coupled receptors and their role in the CNS. New York: Oxford University Press; 2002. pp. 505–526.
-
- Dautzenberg FM, Hauger RL. The CRF peptide family and their receptors: yet more partners discovered. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002;23:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Grigoriadis DE. The corticotropin-releasing factor receptor: a novel target for the treatment of depression and anxiety-related disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005;9:651–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

