A novel role for coenzyme A during hydride transfer in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase
- PMID: 23802607
- PMCID: PMC4007485
- DOI: 10.1021/bi400335g
A novel role for coenzyme A during hydride transfer in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase
Abstract
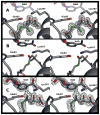
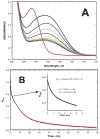
In this study, we take advantage of the ability of HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) from Pseudomonas mevalonii to remain active while in its crystallized form to study the changing interactions between the ligands and protein as the first reaction intermediate is created. HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes one of the few double oxidation-reduction reactions in intermediary metabolism that take place in a single active site. Our laboratory has undertaken an exploration of this reaction space using structures of HMG-CoA reductase complexed with various substrate, nucleotide, product, and inhibitor combinations. With a focus in this publication on the first hydride transfer, our structures follow this reduction reaction as the enzyme converts the HMG-CoA thioester from a flat sp(2)-like geometry to a pyramidal thiohemiacetal configuration consistent with a transition to an sp(3) orbital. This change in the geometry propagates through the coenzyme A (CoA) ligand whose first amide bond is rotated 180° where it anchors a web of hydrogen bonds that weave together the nucleotide, the reaction intermediate, the enzyme, and the catalytic residues. This creates a stable intermediate structure prepared for nucleotide exchange and the second reduction reaction within the HMG-CoA reductase active site. Identification of this reaction intermediate provides a template for the development of an inhibitor that would act as an antibiotic effective against the HMG-CoA reductase of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of the principal catalytically important acidic residue of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase.J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21634-41. J Biol Chem. 1990. PMID: 2123872
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryldithio-coenzyme A: a potent inhibitor of Pseudomonas mevalonii HMG-CoA reductase.Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1991 Apr;45(2):204-8. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(91)90022-d. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1991. PMID: 1679340
-
Biosynthesis and characterization of (S)-and (R)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A.Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1992 Oct;48(2):149-58. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(92)90060-c. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1992. PMID: 1419147
-
The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductases.Genome Biol. 2004;5(11):248. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-11-248. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15535874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signalling functions of coenzyme A and its derivatives in mammalian cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Aug;42(4):1056-62. doi: 10.1042/BST20140146. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25110002 Review.
Cited by
-
An Atomic-Level Perspective of HMG-CoA-Reductase: The Target Enzyme to Treat Hypercholesterolemia.Molecules. 2020 Aug 26;25(17):3891. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173891. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32859023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Crystallographic Snapshots of Large Domain Movements in Bacterial 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase.Biochemistry. 2018 Oct 2;57(39):5715-5725. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00869. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 30199631 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Features and Domain Movements Controlling Substrate Binding and Cofactor Specificity in Class II HMG-CoA Reductase.Biochemistry. 2018 Feb 6;57(5):654-662. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00999. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29224355 Free PMC article.
-
Altered liver expression of genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism in mice with partial IGF-1 deficiency: an experimental approach to metabolic syndrome.J Transl Med. 2015 Oct 14;13:326. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0684-9. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26467524 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Enterococcus faecalis HMG-CoA reductase with a non-statin inhibitor.Commun Biol. 2023 Apr 3;6(1):360. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04639-y. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37012403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Johnson EA, Schroeder WA. Microbial carotenoids. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1996;53:119–178. - PubMed
-
- Reusch VM., Jr Lipopolymers, isoprenoids, and the assembly of the Gram-positive cell wall. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1984;11:129–155. - PubMed
-
- Bochar DA, Stauffacher CV, Rodwell VW. Sequence comparisons reveal two classes of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Mol Genet Metab. 1999;66:122–127. - PubMed
-
- Istvan ES. Bacterial and mammalian HMG-CoA reductases: Related enzymes with distinct architectures. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:746–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

