Early infection HIV-1 envelope V1-V2 genotypes do not enhance binding or replication in cells expressing high levels of α4β7 integrin
- PMID: 23797693
- PMCID: PMC3800220
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182a06ddd
Early infection HIV-1 envelope V1-V2 genotypes do not enhance binding or replication in cells expressing high levels of α4β7 integrin
Abstract
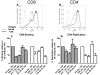
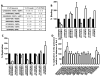
It has been postulated that HIV-1 envelope properties, such as shorter and less-glycosylated V1-V2 loops commonly observed among non-subtype B early-transmitted viruses, promote utilization of the gut homing integrin α4β7. This property potentially confers an advantage to some HIV-1 variants early after acquisition. We found that replication-competent recombinant viruses incorporating HIV-1 subtype A compact and less-glycosylated early versus chronic phase V1-V2 loops demonstrated no significant difference in binding to α4β7 high CD8⁺ T cells or replication in α4β7 high CD4⁺ T cells. Integrin α4β7 usage does not select for shorter less-glycosylated envelopes during transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No author has a commercial or other association that might pose a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of New Regions in HIV-1 gp120 Variable 2 and 3 Loops that Bind to α4β7 Integrin Receptor.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 1;10(12):e0143895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143895. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26625359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transmitted/founder and chronic subtype C HIV-1 use CD4 and CCR5 receptors with equal efficiency and are not inhibited by blocking the integrin α4β7.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(5):e1002686. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002686. Epub 2012 May 31. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22693444 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 V1-V2 envelope loop sequences expand and add glycosylation sites over the course of infection, and these modifications affect antibody neutralization sensitivity.J Virol. 2006 Oct;80(19):9586-98. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00141-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16973562 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 envelope, integrins and co-receptor use in mucosal transmission of HIV.J Transl Med. 2011 Jan 27;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S2. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-S1-S2. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21284901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of T-cell trafficking in the pathogenesis of HIV disease.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2019 Mar;14(2):115-120. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000529. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2019. PMID: 30601238 Review.
Cited by
-
South African HIV-1 subtype C transmitted variants with a specific V2 motif show higher dependence on α4β7 for replication.Retrovirology. 2015 Jun 24;12:54. doi: 10.1186/s12977-015-0183-3. Retrovirology. 2015. PMID: 26105197 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular superspreaders: an epidemiological perspective on HIV infection inside the body.PLoS Pathog. 2014 May 8;10(5):e1004092. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004092. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24811311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tracing HIV-1 transmission: envelope traits of HIV-1 transmitter and recipient pairs.Retrovirology. 2016 Sep 5;13(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0299-0. Retrovirology. 2016. PMID: 27595568 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of HIV-1 envelopes in acutely and chronically infected injection drug users.Retrovirology. 2014 Nov 28;11:106. doi: 10.1186/s12977-014-0106-8. Retrovirology. 2014. PMID: 25430652 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 envelope replication and α4β7 utilization among newly infected subjects and their corresponding heterosexual partners.Retrovirology. 2013 Dec 26;10:162. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-162. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 24369910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haase AT. Perils at mucosal front lines for HIV and SIV and their hosts. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:783–792. - PubMed
-
- Arthos J, Cicala C, Martinelli E, et al. HIV-1 envelope protein binds to and signals through integrin alpha4beta7, the gut mucosal homing receptor for peripheral T cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:301–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

