Distinct chemokine receptor axes regulate Th9 cell trafficking to allergic and autoimmune inflammatory sites
- PMID: 23797668
- PMCID: PMC3721028
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203089
Distinct chemokine receptor axes regulate Th9 cell trafficking to allergic and autoimmune inflammatory sites
Abstract
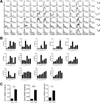
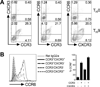
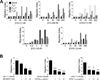
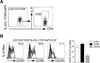
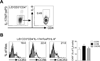
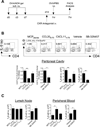
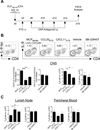
Migration of Th cells to peripheral sites of inflammation is essential for execution of their effector function. The recently described Th9 subset characteristically produces IL-9 and has been implicated in both allergy and autoimmunity. Despite this, the migratory properties of Th9 cells remain enigmatic. In this study, we examined chemokine receptor usage by Th9 cells and demonstrate, in models of allergy and autoimmunity, that these cells express functional CCR3, CCR6, and CXCR3, chemokine receptors commonly associated with other, functionally opposed effector Th subsets. Most Th9 cells that express CCR3 also express CXCR3 and CCR6, and expression of these receptors appears to account for the recruitment of Th9 cells to disparate inflammatory sites. During allergic inflammation, Th9 cells use CCR3 and CCR6, but not CXCR3, to home to the peritoneal cavity, whereas Th9 homing to the CNS during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves CXCR3 and CCR6 but not CCR3. To our knowledge, these data provide the first insights into regulation of Th9 cell trafficking in allergy and autoimmunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Th9 cells in the pathogenesis of EAE and multiple sclerosis.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;39(1):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0604-y. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27844107 Review.
-
C-C chemokine receptor 6-regulated entry of TH-17 cells into the CNS through the choroid plexus is required for the initiation of EAE.Nat Immunol. 2009 May;10(5):514-23. doi: 10.1038/ni.1716. Epub 2009 Mar 22. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19305396
-
Th9 cell development requires a BATF-regulated transcriptional network.J Clin Invest. 2013 Nov;123(11):4641-53. doi: 10.1172/JCI69489. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 24216482 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of chemokine receptors CCR3, CCR5 and CXCR3 on CD4(+) T cells in CBA/JxDBA/2 mouse model, selectively induced by IL-4 and IL-10, regulates the embryo resorption rate.Chin Med J (Engl). 2009 Aug 20;122(16):1917-21. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009. PMID: 19781371
-
Emerging Roles of Th9 Cells as an Anti-tumor Helper T Cells.Int Rev Immunol. 2019;38(5):204-211. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2019.1648453. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Int Rev Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31401904 Review.
Cited by
-
Differentiation and regulation of CD4+ T cell subsets in Parkinson's disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Aug 17;81(1):352. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05402-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39153043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tailored immune responses: novel effector helper T cell subsets in protective immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 20;10(2):e1003905. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003905. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24586147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Aspects and Future Perspectives of Cytokine-Based Anti-cancer Immunotherapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 3;8:402. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00402. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Tissue Resident Memory CD4 T Cells in Herpes Simplex Viral and HIV Infection.Viruses. 2021 Feb 25;13(3):359. doi: 10.3390/v13030359. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33668777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase suppresses allergic lung inflammation by regulating MCP-1 in an OVA-induced asthma murine model with co-exposure to lipopolysaccharide.J Int Med Res. 2020 Feb;48(2):300060520903663. doi: 10.1177/0300060520903663. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32054359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J, Helmby H, Westendorf A, Buer J, Martin B, Wilhelm C, Stockinger B. Transforming growth factor-beta 'reprograms' the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1341–1346. - PubMed
-
- Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Kwon H, Galileos G, Gao W, Sobel RA, Mitsdoerffer M, Strom TB, Elyaman W, Ho IC, Khoury S, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-4 inhibits TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-beta, generates IL-9+ IL-10+ Foxp3(-) effector T cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1347–1355. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng G, Arima M, Honda K, Hirata H, Eda F, Yoshida N, Fukushima F, Ishii Y, Fukuda T. Anti-interleukin-9 antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in mouse asthma model. Am J Respir Criti Care Med. 2002;166:409–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

