Astrocyte regulation of cerebral vascular tone
- PMID: 23792684
- PMCID: PMC3761330
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00359.2013
Astrocyte regulation of cerebral vascular tone
Abstract
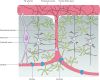
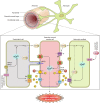
Cerebral blood flow is controlled by two crucial processes, cerebral autoregulation (CA) and neurovascular coupling (NVC) or functional hyperemia. Whereas CA ensures constant blood flow over a wide range of systemic pressures, NVC ensures rapid spatial and temporal increases in cerebral blood flow in response to neuronal activation. The focus of this review is to discuss the cellular mechanisms by which astrocytes contribute to the regulation of vascular tone in terms of their participation in NVC and, to a lesser extent, CA. We discuss evidence for the various signaling modalities by which astrocytic activation leads to vasodilation and vasoconstriction of parenchymal arterioles. Moreover, we provide a rationale for the contribution of astrocytes to pressure-induced increases in vascular tone via the vasoconstrictor 20-HETE (a downstream metabolite of arachidonic acid). Along these lines, we highlight the importance of the transient receptor potential channel of the vanilloid family (TRPV4) as a key molecular determinant in the regulation of vascular tone in cerebral arterioles. Finally, we discuss current advances in the technical tools available to study NVC mechanisms in the brain as it relates to the participation of astrocytes.
Keywords: astrocytes; cerebral autoregulation; neurovascular coupling; parenchymal arteriole; vascular tone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astrocyte contributions to flow/pressure-evoked parenchymal arteriole vasoconstriction.J Neurosci. 2015 May 27;35(21):8245-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4486-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26019339 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond neurovascular coupling, role of astrocytes in the regulation of vascular tone.Neuroscience. 2016 May 26;323:96-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.064. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 25843438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasculo-Neuronal Coupling: Retrograde Vascular Communication to Brain Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Dec 14;36(50):12624-12639. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1300-16.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 7. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27821575 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte Ca2+ Signaling Drives Inversion of Neurovascular Coupling after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 30;35(39):13375-84. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1551-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26424885 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte regulation of blood flow in the brain.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Mar 27;7(5):a020388. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020388. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25818565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control of the neurovascular coupling by nitric oxide-dependent regulation of astrocytic Ca(2+) signaling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Mar 10;9:59. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00059. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25805969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Tools to Study Astrocyte Ca2+ Signal Dynamics in Brain Networks In Vivo.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 May 9;11:134. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00134. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28536505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global and multi-focal changes in cerebral blood flow during subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson's disease.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Apr;38(4):697-705. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17705042. Epub 2017 Apr 19. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 28421851 Free PMC article.
-
Neurovascular coupling mechanisms in health and neurovascular uncoupling in Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2022 Jul 29;145(7):2276-2292. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac174. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35551356 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular profiling of reticular gigantocellularis neurons indicates that eNOS modulates environmentally dependent levels of arousal.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jul 17;115(29):E6900-E6909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806123115. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29967172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 41–53, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Abounader R, Hamel E. Associations between neuropeptide Y nerve terminals and intraparenchymal microvessels in rat and human cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 388: 444–453, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Narayanan J, Gebremedhin D, Medhora M, Roman RJ, Harder DR. Molecular characterization of an arachidonic acid epoxygenase in rat brain astrocytes. Stroke 27: 971–979, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

