CD164 and FCRL3 are highly expressed on CD4+CD26- T cells in Sézary syndrome patients
- PMID: 23792457
- PMCID: PMC3869886
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2013.279
CD164 and FCRL3 are highly expressed on CD4+CD26- T cells in Sézary syndrome patients
Abstract
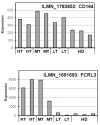
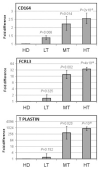
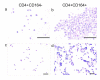
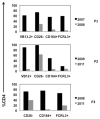
Sézary syndrome (SS) cells express cell surface molecules also found on normal activated CD4 T cells. In an effort to find a more specific surface marker for malignant SS cells, a microarray analysis of gene expression was performed. Results showed significantly increased levels of mRNA for CD164, a sialomucin found on human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells, and FCRL3, a molecule present on a subset of human natural T regulatory cells. Both markers were increased in CD4 T cells from SS patients compared with healthy donors (HD). Flow cytometry studies confirmed the increased expression of CD164 and FCRL3 primarily on CD4+CD26- T cells of SS patients. Importantly, a statistically significant correlation was found between an elevated percentage of CD4+CD164+ T cells and an elevated percentage of CD4+CD26- T cells in all tested SS patients but not in patients with mycosis fungoides and atopic dermatitis or HD. FCRL3 expression was significantly increased only in patients with high tumor burden. CD4+CD164+ cells displayed cerebriform morphology and their loss correlated with clinical improvement in treated patients. Our results suggest that CD164 can serve as a marker for diagnosis and for monitoring progression of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL)/SS and that FCRL3 expression correlates with a high circulating tumor burden.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CD164 identifies CD4+ T cells highly expressing genes associated with malignancy in Sézary syndrome: the Sézary signature genes, FCRL3, Tox, and miR-214.Arch Dermatol Res. 2017 Jan;309(1):11-19. doi: 10.1007/s00403-016-1698-8. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Arch Dermatol Res. 2017. PMID: 27766406 Free PMC article.
-
The relevance of the CD4+ CD26- subset in the identification of circulating Sézary cells.Br J Dermatol. 2001 Jan;144(1):125-35. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04014.x. Br J Dermatol. 2001. PMID: 11167693
-
Expression of CD164 on Malignant T cells in Sézary Syndrome.Acta Derm Venereol. 2016 May;96(4):464-7. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2264. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016. PMID: 26524186
-
Identification of cell surface molecules characterizing human cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.Leuk Lymphoma. 2002 Apr;43(4):741-6. doi: 10.1080/10428190290016836. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002. PMID: 12153159 Review.
-
Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part I. Diagnosis: clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Feb;70(2):205.e1-16; quiz 221-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.049. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24438969 Review.
Cited by
-
High Expression of IKZF2 in Malignant T Cells Promotes Disease Progression in Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma.Acta Derm Venereol. 2021 Dec 7;101(12):adv00613. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v101.570. Acta Derm Venereol. 2021. PMID: 34853863 Free PMC article.
-
Stilbenoids remodel the DNA methylation patterns in breast cancer cells and inhibit oncogenic NOTCH signaling through epigenetic regulation of MAML2 transcriptional activity.Carcinogenesis. 2016 Jul;37(7):656-68. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgw048. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Carcinogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27207652 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of CD164 in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma predicts a favourable prognosis.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):6103-6108. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6966. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113253 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Sézary syndrome and lymphocytic-variant hypereosinophilic syndrome T cells reveals common and divergent genes.Oncotarget. 2019 Aug 20;10(49):5052-5069. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27120. eCollection 2019 Aug 20. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31489115 Free PMC article.
-
The biomarker landscape in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome.Exp Dermatol. 2017 Aug;26(8):668-676. doi: 10.1111/exd.13261. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27897325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bensussan A, Remtoula N, Sivori S, et al. Expression and function of the natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp46 on circulating malignant CD4+ T lymphocytes of Sezary syndrome patients. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:969–76. - PubMed
-
- Bernengo MG, Novelli M, Quaglino P, et al. The relevance of the CD4+ CD26− subset in the identification of circulating Sezary cells. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:125–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

