The spindle checkpoint, APC/C(Cdc20), and APC/C(Cdh1) play distinct roles in connecting mitosis to S phase
- PMID: 23775192
- PMCID: PMC3691463
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201211019
The spindle checkpoint, APC/C(Cdc20), and APC/C(Cdh1) play distinct roles in connecting mitosis to S phase
Abstract
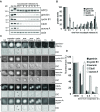
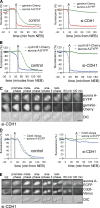
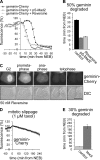
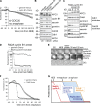
DNA replication depends on a preceding licensing event by Cdt1 and Cdc6. In animal cells, relicensing after S phase but before mitosis is prevented by the Cdt1 inhibitor geminin and mitotic cyclin activity. Here, we show that geminin, like cyclin B1 and securin, is a bona fide target of the spindle checkpoint and APC/C(Cdc20). Cyclin B1 and geminin are degraded simultaneously during metaphase, which directs Cdt1 accumulation on segregating sister chromatids. Subsequent activation of APC/C(Cdh1) leads to degradation of Cdc6 well before Cdt1 becomes unstable in a replication-coupled manner. In mitosis, the spindle checkpoint supports Cdt1 accumulation, which promotes S phase onset. We conclude that the spindle checkpoint, APC/C(Cdc20), and APC/C(Cdh1) act successively to ensure that the disappearance of licensing inhibitors coincides exactly with a peak of Cdt1 and Cdc6. Whereas cell cycle entry from quiescence requires Cdc6 resynthesis, our results indicate that proliferating cells use a window of time in mitosis, before Cdc6 is degraded, as an earlier opportunity to direct S phase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The regulation of Cdc20 proteolysis reveals a role for APC components Cdc23 and Cdc27 during S phase and early mitosis.Curr Biol. 1998 Jun 18;8(13):750-60. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70298-2. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9651679
-
To cell cycle, swing the APC/C.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Sep;1786(1):49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.05.002. Epub 2008 May 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18544349 Review.
-
The APC/C recruits cyclin B1-Cdk1-Cks in prometaphase before D box recognition to control mitotic exit.J Cell Biol. 2010 Aug 23;190(4):587-602. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912084. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20733055 Free PMC article.
-
How APC/C-Cdc20 changes its substrate specificity in mitosis.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Mar;13(3):223-33. doi: 10.1038/ncb2165. Epub 2011 Feb 20. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21336306 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin A and Nek2A: APC/C-Cdc20 substrates invisible to the mitotic spindle checkpoint.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):72-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0380072. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074038 Review.
Cited by
-
The Insulin Receptor Adaptor IRS2 is an APC/C Substrate That Promotes Cell Cycle Protein Expression and a Robust Spindle Assembly Checkpoint.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Sep;19(9):1450-1467. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002069. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32554797 Free PMC article.
-
Counting Degrons: Lessons From Multivalent Substrates for Targeted Protein Degradation.Front Physiol. 2022 Jul 4;13:913063. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.913063. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35860655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP1-dependent recruitment of the FBXL10-RNF68-RNF2 ubiquitin ligase to sites of DNA damage controls H2A.Z loading.Elife. 2018 Jul 9;7:e38771. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38771. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29985131 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Radiobiology of Vestibular Schwannomas to Overcome Radiation Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 12;13(18):4575. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184575. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ordered dephosphorylation initiated by the selective proteolysis of cyclin B drives mitotic exit.Elife. 2020 Sep 1;9:e59885. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59885. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32869743 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

