Protease inhibitors from marine venomous animals and their counterparts in terrestrial venomous animals
- PMID: 23771044
- PMCID: PMC3721222
- DOI: 10.3390/md11062069
Protease inhibitors from marine venomous animals and their counterparts in terrestrial venomous animals
Abstract
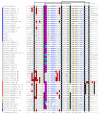
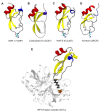
The Kunitz-type protease inhibitors are the best-characterized family of serine protease inhibitors, probably due to their abundance in several organisms. These inhibitors consist of a chain of ~60 amino acid residues stabilized by three disulfide bridges, and was first observed in the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI)-like protease inhibitors, which strongly inhibit trypsin and chymotrypsin. In this review we present the protease inhibitors (PIs) described to date from marine venomous animals, such as from sea anemone extracts and Conus venom, as well as their counterparts in terrestrial venomous animals, such as snakes, scorpions, spiders, Anurans, and Hymenopterans. More emphasis was given to the Kunitz-type inhibitors, once they are found in all these organisms. Their biological sources, specificity against different proteases, and other molecular blanks (being also K+ channel blockers) are presented, followed by their molecular diversity. Whereas sea anemone, snakes and other venomous animals present mainly Kunitz-type inhibitors, PIs from Anurans present the major variety in structure length and number of Cys residues, with at least six distinguishable classes. A representative alignment of PIs from these venomous animals shows that, despite eventual differences in Cys assignment, the key-residues for the protease inhibitory activity in all of them occupy similar positions in primary sequence. The key-residues for the K+ channel blocking activity was also compared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A bifunctional sea anemone peptide with Kunitz type protease and potassium channel inhibiting properties.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Jul 1;82(1):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.03.023. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21477583
-
The Kunitz-Type Protein ShPI-1 Inhibits Serine Proteases and Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Apr 13;8(4):110. doi: 10.3390/toxins8040110. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27089366 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Aspects of the Structural Convergence and Functional Diversification of Kunitz-Domain Inhibitors.J Mol Evol. 2020 Sep;88(7):537-548. doi: 10.1007/s00239-020-09959-9. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Mol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32696206 Review.
-
SdPI, the first functionally characterized Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor from scorpion venom.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027548. Epub 2011 Nov 8. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22087336 Free PMC article.
-
Venom-derived peptide inhibitors of voltage-gated potassium channels.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Dec;127:124-138. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28689025 Review.
Cited by
-
The Transcriptome of the Zoanthid Protopalythoa variabilis (Cnidaria, Anthozoa) Predicts a Basal Repertoire of Toxin-like and Venom-Auxiliary Polypeptides.Genome Biol Evol. 2016 Oct 5;8(9):3045-3064. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw204. Genome Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27566758 Free PMC article.
-
A RNA-seq approach to identify putative toxins from acrorhagi in aggressive and non-aggressive Anthopleura elegantissima polyps.BMC Genomics. 2015 Mar 21;16(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1417-4. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25886045 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Pseudoscorpion Venom Reveals a Unique Cocktail Dominated by Enzymes and Protease Inhibitors.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 18;10(5):207. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050207. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29783636 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analyses of venom from a Spider Hawk, Pepsis decorata.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2023 Nov 10;29:e20220090. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2022-0090. eCollection 2023. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37965483 Free PMC article.
-
A Versatile and Robust Serine Protease Inhibitor Scaffold from Actinia tenebrosa.Mar Drugs. 2019 Dec 12;17(12):701. doi: 10.3390/md17120701. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31842369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliva M.L., Souza-Pinto J.C., Batista I.F., Araujo M.S., Silveira V.F., Auerswald E.A., Mentele R., Eckerskorn C., Sampaio M.U., Sampaio C.A. Leucaena leucocephala serine proteinase inhibitor: Primary structure and action on blood coagulation, kinin release and rat paw edema. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1477:64–74. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4838(99)00285-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

