A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence
- PMID: 23770676
- PMCID: PMC3732483
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2784
A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence
Abstract
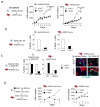
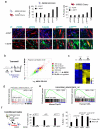
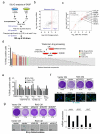
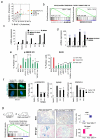
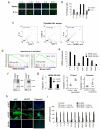
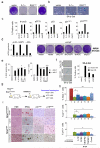
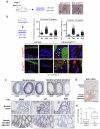
Oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) is crucial for tumour suppression. Senescent cells implement a complex pro-inflammatory response termed the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The SASP reinforces senescence, activates immune surveillance and paradoxically also has pro-tumorigenic properties. Here, we present evidence that the SASP can also induce paracrine senescence in normal cells both in culture and in human and mouse models of OIS in vivo. Coupling quantitative proteomics with small-molecule screens, we identified multiple SASP components mediating paracrine senescence, including TGF-β family ligands, VEGF, CCL2 and CCL20. Amongst them, TGF-β ligands play a major role by regulating p15(INK4b) and p21(CIP1). Expression of the SASP is controlled by inflammasome-mediated IL-1 signalling. The inflammasome and IL-1 signalling are activated in senescent cells and IL-1α expression can reproduce SASP activation, resulting in senescence. Our results demonstrate that the SASP can cause paracrine senescence and impact on tumour suppression and senescence in vivo.
Figures

Comment in
-
Senescent cells spread the word: non-cell autonomous propagation of cellular senescence.EMBO J. 2013 Jul 17;32(14):1975-6. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.139. Epub 2013 Jun 18. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23778965 Free PMC article.
-
Transmitting senescence to the cell neighbourhood.Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;15(8):887-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb2811. Nat Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23907191
Similar articles
-
Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma as a model to understand paracrine and senescence-induced tumourigenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(10):4521-4544. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03798-7. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34019103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor suppressor and aging biomarker p16(INK4a) induces cellular senescence without the associated inflammatory secretory phenotype.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 21;286(42):36396-403. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.257071. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21880712 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype from Cell Cycle Exit via Interleukin-1 Inactivation Unveils Its Protumorigenic Role.Mol Cell Biol. 2019 May 28;39(12):e00586-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00586-18. Print 2019 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30988157 Free PMC article.
-
The protein kinase D1-mediated classical protein secretory pathway regulates the Ras oncogene-induced senescence response.J Cell Sci. 2018 Mar 16;131(6):jcs207217. doi: 10.1242/jcs.207217. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29420297
-
Regulation of senescence and the SASP by the transcription factor C/EBPβ.Exp Gerontol. 2019 Dec;128:110752. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.110752. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Exp Gerontol. 2019. PMID: 31648009 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune therapeutic strategies for the senescent tumor microenvironment.Br J Cancer. 2024 Oct 28. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02865-7. Online ahead of print. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39468331 Review.
-
Association between magnesium depletion score and periodontitis in US adults: results from NHANES 2009-2014.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 24;24(1):1274. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05048-1. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39448970 Free PMC article.
-
Cell senescence in cardiometabolic diseases.NPJ Aging. 2024 Oct 21;10(1):46. doi: 10.1038/s41514-024-00170-4. NPJ Aging. 2024. PMID: 39433786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia and aging: molecular mechanisms, diseases, and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 15;5(11):e786. doi: 10.1002/mco2.786. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39415849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammaging and Brain Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;25(19):10535. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910535. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

