Dual oxidase regulates neutrophil recruitment in allergic airways
- PMID: 23770197
- PMCID: PMC3859817
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.012
Dual oxidase regulates neutrophil recruitment in allergic airways
Abstract
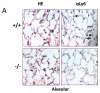
Enhanced reactive oxygen species production in allergic airways is well described and correlates with increased airway contractions, inflammatory cell infiltration, goblet cell metaplasia, and mucus hypersecretion. There is also an abundance of interleukin-4/interleukin-13 (IL-4/IL-13)- or interleukin-5-secreting cells that are thought to be central to the pathogenesis of allergic asthma. We postulated that the dual oxidases (DUOX1 and DUOX2), members of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase family that release hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the respiratory tract, are critical proteins in the pathogenesis of allergic airways. DUOX activity is regulated by cytokines, including IL-4 and IL-13, and DUOX-mediated H2O2 influences several important features of allergic asthma: mucin production, IL-8 secretion, and wound healing. The objective of this study was to establish the contribution of DUOXs to the development of allergic asthma in a murine model. To accomplish this goal, we utilized a DUOXA-deficient mouse model (Duoxa(-/-)) that lacked maturation factors for both DUOX1 and DUOX2. Our results are the first to demonstrate evidence of DUOX protein and DUOX functional activity in murine airway epithelium. We also demonstrate that DUOXA maturation factors are required for airway-specific H2O2 production and localization of DUOX to cilia of fully differentiated airway epithelial cells. We compared wild-type and Duoxa(-/-) mice in an ovalbumin exposure model to determine the role of DUOX in allergic asthma. In comparison to DUOX-intact mice, Duoxa(-/-) mice had reduced mucous cell metaplasia and lower levels of TH2 cytokine levels in bronchoalveolar fluid. In addition, increased airway resistance in response to methacholine was observed in Duoxa(+/+) mice, as expected, but was absent in Duoxa(-/-) mice. Surprisingly, Duoxa(-/-) mice had decreased influx of neutrophils in bronchoalveolar fluid and lung tissue sections associated with a lower level of the chemotactic cytokine IL-6. These findings suggest that DUOX-derived H2O2 has an important role in signaling neutrophils into allergic airways.
Keywords: Asthma; BALF; DPI; DUOX; Dual oxidase; Free radicals; IL; L-T(4); Lung; Murine; Neutrophil; ROS; T(H); T-helper cell; TLR; Toll-like receptor; bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; diphenyleneiodonium; dual oxidase; interleukin; levothyroxine; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


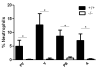
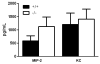
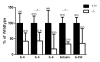
Similar articles
-
Dual oxidases control release of hydrogen peroxide by the gastric epithelium to prevent Helicobacter felis infection and inflammation in mice.Gastroenterology. 2013 Nov;145(5):1045-54. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.07.011. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23860501 Free PMC article.
-
Mice deficient in dual oxidase maturation factors are severely hypothyroid.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Mar;26(3):481-92. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1320. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22301785 Free PMC article.
-
Heterodimerization controls localization of Duox-DuoxA NADPH oxidases in airway cells.J Cell Sci. 2009 Apr 15;122(Pt 8):1238-47. doi: 10.1242/jcs.044123. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19339556 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and function of DUOX in epithelia of the lung.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009 Oct;11(10):2453-65. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2558. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009. PMID: 19358684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of DUOX-mediated hydrogen peroxide in metabolism, host defense, and signaling.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jun 10;20(17):2776-93. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5602. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24161126 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteinase activated receptor-2-mediated dual oxidase-2 up-regulation is involved in enhanced airway reactivity and inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma.Immunology. 2015 Jul;145(3):391-403. doi: 10.1111/imm.12453. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25684443 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial actions of dual oxidases and lactoperoxidase.J Microbiol. 2018 Jun;56(6):373-386. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-7545-1. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29858825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy regulates DUOX1 localization and superoxide production in airway epithelial cells during chronic IL-13 stimulation.Redox Biol. 2018 Apr;14:272-284. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 28982074 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Tissue Damage and Microbial Cues Drive Neutrophil and Macrophage Recruitment to Thermal Injury.iScience. 2020 Oct 22;23(11):101699. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101699. eCollection 2020 Nov 20. iScience. 2020. PMID: 33196024 Free PMC article.
-
Thiol redox chemistry: role of protein cysteine oxidation and altered redox homeostasis in allergic inflammation and asthma.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Jun;116(6):884-92. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25017. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25565397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holgate ST. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nature medicine. 2012;18:673–683. - PubMed
-
- Hammad H, Lambrecht BN. Dendritic cells and airway epithelial cells at the interface between innate and adaptive immune responses. Allergy. 2011;66:579–587. - PubMed
-
- Larche M. Regulatory T cells in allergy and asthma. Chest. 2007;132:1007–1014. - PubMed
-
- Reuter S, Dehzad N, Martin H, Bohm L, Becker M, Buhl R, Stassen M, Taube C. TLR3 but not TLR7/8 ligand induces allergic sensitization to inhaled allergen. J Immunol. 2012;188:5123–5131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

