eIF3f: a central regulator of the antagonism atrophy/hypertrophy in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 23769948
- PMCID: PMC7108353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.001
eIF3f: a central regulator of the antagonism atrophy/hypertrophy in skeletal muscle
Abstract
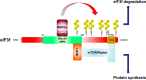
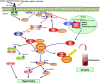
The eukaryotic initiation factor 3 subunit f (eIF3f) is one of the 13 subunits of the translation initiation factor complex eIF3 required for several steps in the initiation of mRNA translation. In skeletal muscle, recent studies have demonstrated that eIF3f plays a central role in skeletal muscle size maintenance. Accordingly, eIF3f overexpression results in hypertrophy through modulation of protein synthesis via the mTORC1 pathway. Importantly, eIF3f was described as a target of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MAFbx/atrogin-1 for proteasome-mediated breakdown under atrophic conditions. The biological importance of the MAFbx/atrogin-1-dependent targeting of eFI3f is highlighted by the finding that expression of an eIF3f mutant insensitive to MAFbx/atrogin-1 polyubiquitination is associated with enhanced protection against starvation-induced muscle atrophy. A better understanding of the precise role of this subunit should lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches to prevent or limit muscle wasting that prevails in numerous physiological and pathological states such as immobilization, aging, denervated conditions, neuromuscular diseases, AIDS, cancer, diabetes. This article is part of a Directed Issue entitled: Molecular basis of muscle wasting.
Keywords: Cell growth; MAFbx/atrogin-1; Protein translation; Skeletal muscle; eIF3f.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MAFbx/Atrogin-1 controls the activity of the initiation factor eIF3-f in skeletal muscle atrophy by targeting multiple C-terminal lysines.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 13;284(7):4413-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807641200. Epub 2008 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19073596
-
eIF3-f function in skeletal muscles: to stand at the crossroads of atrophy and hypertrophy.Cell Cycle. 2008 Jun 15;7(12):1698-701. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.12.6090. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18583931
-
eIF3f depletion impedes mouse embryonic development, reduces adult skeletal muscle mass and amplifies muscle loss during disuse.J Physiol. 2019 Jun;597(12):3107-3131. doi: 10.1113/JP277841. Epub 2019 May 15. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31026345
-
Glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2163-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.036. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23806868 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms modulating muscle mass.Trends Mol Med. 2003 Aug;9(8):344-50. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4914(03)00138-2. Trends Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12928036 Review.
Cited by
-
A DGKζ-FoxO-ubiquitin proteolytic axis controls fiber size during skeletal muscle remodeling.Sci Signal. 2018 May 15;11(530):eaao6847. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aao6847. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 29764991 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Diagnostic Deubiquitinating Enzymes in Endometriosis and Its Immune Infiltration.Biochem Genet. 2024 Dec;62(6):4359-4379. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10653-w. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38302849
-
The impact of heat therapy on neuromuscular function and muscle atrophy in diabetic rats.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1039588. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1039588. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36685197 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting eIF3f Suppresses the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Akt Signaling.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 4;13:3739-3750. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S244345. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32440143 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Mitigates the Loss of Muscle Mass by Attenuating the Activation of Autophagy during Severe Energy Deficit.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 19;11(11):2824. doi: 10.3390/nu11112824. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31752260 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Asano K., Vornlocher H.P., Richter-Cook N.J., Merrick W.C., Hinnebusch A.G., Hershey J.W. Structure of cDNAs encoding human eukaryotic initiation factor 3 subunits. Possible roles in RNA binding and macromolecular assembly. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272:27042–27052. - PubMed
-
- Attaix D., Baracos V.E., Pichard C. Muscle wasting: a crosstalk between protein synthesis and breakdown signalling. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 2012;15:209–210. - PubMed
-
- Bodine S.C., Latres E., Baumhueter S., Lai V.K., Nunez L., Clarke B.A. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science. 2001;294:1704–1708. - PubMed
-
- Csibi A., Leibovitch M.P., Cornille K., Tintignac L.A., Leibovitch S.A. MAFbx/Atrogin-1 controls the activity of the initiation factor eIF3-f in skeletal muscle atrophy by targeting multiple C-terminal lysines. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009;284:4413–4421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

