Cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory protein (CARP)-1 is expressed in osteoblasts and regulated by PTH
- PMID: 23764399
- PMCID: PMC3737602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.136
Cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory protein (CARP)-1 is expressed in osteoblasts and regulated by PTH
Abstract
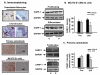
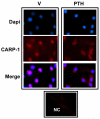
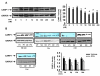
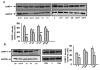
Bone mass is dependent on osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and life-span of osteoblasts. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) controls osteoblast cell cycle regulatory proteins and suppresses mature osteoblasts apoptosis. Intermittent administration of PTH increases bone mass but the mechanism of action are complex and incompletely understood. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Regulatory Protein (CARP)-1 (aka CCAR1) is a novel transducer of signaling by diverse agents including cell growth and differentiation factors. To gain further insight into the molecular mechanism, we investigated involvement of CARP-1 in PTH signaling in osteoblasts. Immunostaining studies revealed presence of CARP-1 in osteoblasts and osteocytes, while a minimal to absent levels were noted in the chondrocytes of femora from 10 to 12-week old mice. Treatment of 7-day differentiated MC3T3-E1 clone-4 (MC-4) mouse osteoblastic cells and primary calvarial osteoblasts with PTH for 30min to 5h followed by Western blot analysis showed 2- to 3-fold down-regulation of CARP-1 protein expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner compared to the respective vehicle treated control cells. H-89, a Protein Kinase A (PKA) inhibitor, suppressed PTH action on CARP-1 protein expression indicating PKA-dependent mechanism. PMA, a Protein Kinase C (PKC) agonist, mimicked PTH action, and the PKC inhibitor, GF109203X, partially blocked PTH-dependent downregulation of CARP-1, implying involvement of PKC. U0126, a Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Kinase (MEK) inhibitor, failed to interfere with CARP-1 suppression by PTH. In contrast, SB203580, p38 inhibitor, attenuated PTH down-regulation of CARP-1 suggesting that PTH utilized an Extracellular Signal Regulated Kinase (ERK)-independent but p38 dependent pathway to regulate CARP-1 protein expression in osteoblasts. Immunofluorescence staining of differentiated osteoblasts further revealed nuclear to cytoplasmic translocation of CARP-1 protein following PTH treatment. Collectively, our studies identified CARP-1 for the first time in osteoblasts and suggest its potential role in PTH signaling and bone anabolic action.
Keywords: CARP-1; Differentiation; EDTA; ERK; MAPK; MAPK kinase; MC-4; MC3T3-E1 clone 4; MEK; Osteoblast; PKA; PKC; PMA; PTH; PTH receptor-1; PTHR1; cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory protein -1; ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid; extracellular signal regulated kinase; mitogen-activated protein kinase; parathyroid hormone; phorbol-12-myristate-13 acetate; protein kinase A; protein kinase C.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PTHrP signaling targets cyclin D1 and induces osteoblastic cell growth arrest.J Bone Miner Res. 2005 Jun;20(6):1051-64. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.050106. Epub 2005 Jan 18. J Bone Miner Res. 2005. PMID: 15883646
-
Regulation of matrix Gla protein by parathyroid hormone in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells involves protein kinase A and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Oct 1;102(2):496-505. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21314. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17407158
-
Distinct roles for mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and ERK-MAPK in PTH1R signaling during osteoblast proliferation and differentiation.Cell Signal. 2010 Mar;22(3):457-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.10.017. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 19892016 Free PMC article.
-
Parathyroid hormone-dependent signaling pathways regulating genes in bone cells.Gene. 2002 Jan 9;282(1-2):1-17. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00798-3. Gene. 2002. PMID: 11814673 Review.
-
The roles of parathyroid hormone in bone remodeling: prospects for novel therapeutics.J Endocrinol Invest. 2011 Jul;34(7 Suppl):18-22. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011. PMID: 21985975 Review.
Cited by
-
PTHrP attenuates osteoblast cell death and apoptosis induced by a novel class of anti-cancer agents.Endocrine. 2016 Mar;51(3):534-44. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0699-2. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 26260694
-
Angelica polysaccharide promotes proliferation and osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by regulation of long non-coding RNA H19: An animal study.Bone Joint Res. 2019 Aug 2;8(7):323-332. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.87.BJR-2018-0223.R2. eCollection 2019 Jul. Bone Joint Res. 2019. PMID: 31463041 Free PMC article.
-
PTH and the Regulation of Mesenchymal Cells within the Bone Marrow Niche.Cells. 2024 Feb 26;13(5):406. doi: 10.3390/cells13050406. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p38 MAPK Signaling in Osteoblast Differentiation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 May 6;4:40. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00040. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27200351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CARP-1/CCAR1: a biphasic regulator of cancer cell growth and apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):6499-510. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3376. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25894788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lian JB, Stein GS, Aubin JE. Bone formation: maturation and functional activities of osteoblast lineage cells. In: Favus MJ, editor. Primer on the metabolic bone diseases and disorders of mineral metabolism. American Society for Bone and Mineral Research; Washington: 2003. pp. 13–28.
-
- Hock JM, Fitzpatrick LA, Bilezikian JP. Actions of Parathyroid Hormone. In: Bilezikian JP, Raisz LG, Rodan GA, Bilezikian JP, Raisz LG, Rodan GA, editors. Principles of Bone Biology. Principles of Bone Biology. 2nd ed. 2nd ed. Academic Press; Academic Press; San Diego: San Diego: 2002. pp. 463–482.
-
- Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, Prince R, Gaich GA, Reginster JY, Hodsman AB, Eriksen EF, Ish-Shalom S, Genant HK, Wang O, Mitlak BH. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1-34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1434–1441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

