Speciation, phenotypic variation and plasticity: what can endocrine disruptors tell us?
- PMID: 23762055
- PMCID: PMC3670528
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/862739
Speciation, phenotypic variation and plasticity: what can endocrine disruptors tell us?
Abstract
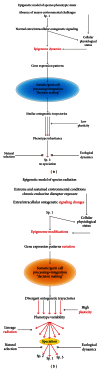
Phenotype variability, phenotypic plasticity, and the inheritance of phenotypic traits constitute the fundamental ground of processes such as individuation, individual and species adaptation and ultimately speciation. Even though traditional evolutionary thinking relies on genetic mutations as the main source of intra- and interspecies phenotypic variability, recent studies suggest that the epigenetic modulation of gene transcription and translation, epigenetic memory, and epigenetic inheritance are by far the most frequent reliable sources of transgenerational variability among viable individuals within and across organismal species. Therefore, individuation and speciation should be considered as nonmutational epigenetic phenomena.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of non-genetic inheritance in evolutionary rescue: epigenetic buffering, heritable bet hedging and epigenetic traps.Environ Epigenet. 2016 Feb 15;2(1):dvv014. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvv014. eCollection 2016 Jan. Environ Epigenet. 2016. PMID: 29492283 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic induction may speed up or slow down speciation with gene flow.Evolution. 2022 Jun;76(6):1170-1182. doi: 10.1111/evo.14494. Epub 2022 May 1. Evolution. 2022. PMID: 35482931 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational inheritance: how impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):518-540. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz017. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31374565
-
Epigenetic Inheritance across the Landscape.Front Genet. 2016 Oct 25;7:189. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00189. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27826318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic plasticity and diversity in insects.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010 Feb 27;365(1540):593-603. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0263. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20083635 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phthalate Exposure and Long-Term Epigenomic Consequences: A Review.Front Genet. 2020 May 6;11:405. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00405. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32435260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal Exposure to Phthalates: From Endocrine to Neurodevelopment Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 14;22(8):4063. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084063. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Male Ejaculatory Endophenotypes: Revealing Internal Inconsistencies of the Concept in Heterosexual Copulating Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Jun 26;14:90. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00090. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32670030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peabody DC, Peabody RB, Tyrrell MG, Towle MJ, Johnson EM. Phenotypic plasticity and evolutionary potential in somatic cells of Armillaria gallica. Mycological Research. 2003;107(4):408–412. - PubMed
-
- Wagner CR. Germ cells and epigenetics. Nature Education. 2010;3(9):p. 64.
-
- Surani MA, Ancelin K, Hajkova P, et al. Mechanism of mouse germ cell specification: a genetic program regulating epigenetic reprogramming. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 2004;69:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Jaenisch R, Hochedlinger K, Blelloch R, Yamada Y, Baldwin K, Eggan K. Nuclear cloning, epigenetic reprogramming, and cellular differentiation. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 2004;69:19–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

