Molecular properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
- PMID: 23759942
- PMCID: PMC3749793
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.89.226
Molecular properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Abstract
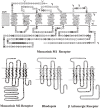
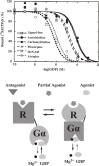
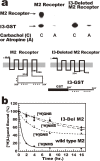
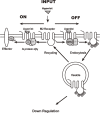
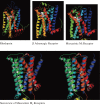
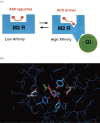
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, which comprise five subtypes (M1-M5 receptors), are expressed in both the CNS and PNS (particularly the target organs of parasympathetic neurons). M1-M5 receptors are integral membrane proteins with seven transmembrane segments, bind with acetylcholine (ACh) in the extracellular phase, and thereafter interact with and activate GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) in the intracellular phase: M1, M3, and M5 receptors interact with Gq-type G proteins, and M2 and M4 receptors with Gi/Go-type G proteins. Activated G proteins initiate a number of intracellular signal transduction systems. Agonist-bound muscarinic receptors are phosphorylated by G protein-coupled receptor kinases, which initiate their desensitization through uncoupling from G proteins, receptor internalization, and receptor breakdown (down regulation). Recently the crystal structures of M2 and M3 receptors were determined and are expected to contribute to the development of drugs targeted to muscarinic receptors. This paper summarizes the molecular properties of muscarinic receptors with reference to the historical background and bias to studies performed in our laboratories.
Figures


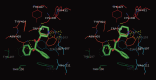
Similar articles
-
Understanding G Protein Selectivity of Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors Using Computational Methods.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 24;20(21):5290. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215290. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31653051 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal tail of the M3-muscarinic receptor possesses anti-apoptotic properties.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 23;278(21):19565-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211670200. Epub 2003 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12649280
-
The allosteric site regulates the voltage sensitivity of muscarinic receptors.Cell Signal. 2018 Jan;42:114-126. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29056499
-
Heartfelt crosstalk: desensitization of the GIRK current.Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;2(9):E165-7. doi: 10.1038/35023646. Nat Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10980715 Review. No abstract available.
-
Muscarinic receptor subtypes in the alimentary tract.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;60(1):3-21. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19439804 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the neurotransmitter system associated with cognitive function of the cerebellum in Parkinson's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Feb;19(2):324-330. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.379042. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term exposure to muscarinic agonists decreases expression of contractile proteins and responsiveness of rabbit tracheal smooth muscle cells.BMC Pulm Med. 2014 Mar 10;14:39. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-39. BMC Pulm Med. 2014. PMID: 24607024 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Type 1 Receptor Activity Constrains Neurite Outgrowth by Inhibiting Microtubule Polymerization and Mitochondrial Trafficking in Adult Sensory Neurons.Front Neurosci. 2018 Jun 26;12:402. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00402. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29997469 Free PMC article.
-
The retrotrapezoid nucleus and the neuromodulation of breathing.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Mar 1;125(3):699-719. doi: 10.1152/jn.00497.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 2. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33427575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discrete localization of phospholipase Cβ3 and diacylglycerol kinase ι along the renal proximal tubules of normal rat kidney and gentamicin-induced changes in their expression.Histochem Cell Biol. 2023 Mar;159(3):293-307. doi: 10.1007/s00418-022-02166-1. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Histochem Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36478081
References
-
- Dale H.H. (1914) The action of certain esters and ethers of choline, and their relation to muscarine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 6, 147–190
-
- Nieuwenhuys, R. (1985) Chemoarchitecture of the Brain, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 7–11.
-
- Birdsall N.J.M., Hulme E.C. (1976) Biochemical studies on muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurochem. 27, 7–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

