Agp2, a member of the yeast amino acid permease family, positively regulates polyamine transport at the transcriptional level
- PMID: 23755272
- PMCID: PMC3670898
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065717
Agp2, a member of the yeast amino acid permease family, positively regulates polyamine transport at the transcriptional level
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(7). doi:10.1371/annotation/ff0ad3b6-fff4-4783-8c2e-968a95283ab8. Rubio Texeira, Marta [corrected to Rubio-Texeira, Marta]
Abstract
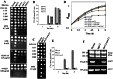
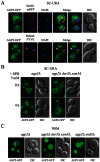
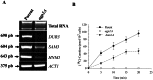
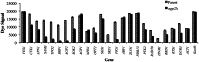
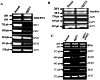
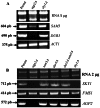
Agp2 is a plasma membrane protein of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae amino acid transporter family, involved in high-affinity uptake of various substrates including L-carnitine and polyamines. The discovery of two high affinity polyamine permeases, Dur3 and Sam3, prompted us to investigate whether Agp2 directly transports polyamines or acts instead as a regulator. Herein, we show that neither dur3Δ nor sam3Δ single mutant is defective in polyamine transport, while the dur3Δ sam3Δ double mutant exhibits a sharp decrease in polyamine uptake and an increased resistance to polyamine toxicity similar to the agp2Δ mutant. Studies of Agp2 localization indicate that in the double mutant dur3Δ sam3Δ, Agp2-GFP remains plasma membrane-localized, even though transport of polyamines is strongly reduced. We further demonstrate that Agp2 controls the expression of several transporter genes including DUR3 and SAM3, the carnitine transporter HNM1 and several hexose, nucleoside and vitamin permease genes, in addition to SKY1 encoding a SR kinase that positively regulates low-affinity polyamine uptake. Furthermore, gene expression analysis clearly suggests that Agp2 is a strong positive regulator of additional biological processes. Collectively, our data suggest that Agp2 might respond to environmental cues and thus regulate the expression of several genes including those involved in polyamine transport.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
AGP2 encodes the major permease for high affinity polyamine import in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 24;280(25):24267-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503071200. Epub 2005 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15855155
-
Polyamine uptake by DUR3 and SAM3 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7733-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611105200. Epub 2007 Jan 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17218313
-
Complementation of the Yeast Model System Reveals that Caenorhabditis elegans OCT-1 Is a Functional Transporter of Anthracyclines.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0133182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133182. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26177450 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of cellular polyamine transport in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010 Jul;48(7):506-12. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.01.017. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20159658 Review.
-
Sugar and Glycerol Transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;892:125-168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25304-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26721273 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel findings about the mode of action of the antifungal protein PeAfpA against Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;107(22):6811-6829. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12749-0. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37688596 Free PMC article.
-
The Yeast Permease Agp2 Senses Cycloheximide and Undergoes Degradation That Requires the Small Protein Brp1-Cellular Fate of Agp2 in Response to Cycloheximide.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 10;24(8):6975. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086975. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108141 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative reactions at the interface of glycolysis and citric acid cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Yeast Res. 2016 May;16(3):fow017. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/fow017. Epub 2016 Feb 18. FEMS Yeast Res. 2016. PMID: 26895788 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for Carnitine Shuttle-Mediated Translocation of Mitochondrial Acetyl Moieties to the Yeast Cytosol.mBio. 2016 May 3;7(3):e00520-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00520-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27143389 Free PMC article.
-
Translational autoregulation of the S. cerevisiae high-affinity polyamine transporter Hol1.Mol Cell. 2021 Oct 7;81(19):3904-3918.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.020. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34375581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schreve JL, Garrett JM (2004) Yeast Agp2p and Agp3p function as amino acid permeases in poor nutrient conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313: 745–751. - PubMed
-
- Iraqui I, Vissers S, Bernard F, de Craene JO, Boles E, et al. (1999) Amino acid signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a permease-like sensor of external amino acids and F-Box protein Grr1p are required for transcriptional induction of the AGP1 gene, which encodes a broad-specificity amino acid permease. Mol Cell Biol 19: 989–1001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Roermund CW, Hettema EH, van den Berg M, Tabak HF, Wanders RJ (1999) Molecular characterization of carnitine-dependent transport of acetyl-CoA from peroxisomes to mitochondria in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and identification of a plasma membrane carnitine transporter, Agp2p. Embo J 18: 5843–5852. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee J, Lee B, Shin D, Kwak SS, Bahk JD, et al. (2002) Carnitine uptake by AGP2 in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is dependent on Hog1 MAP kinase pathway. Mol Cells 13: 407–412. - PubMed
-
- Aouida M, Page N, Leduc A, Peter M, Ramotar D (2004) A Genome-Wide Screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Reveals Altered Transport As a Mechanism of Resistance to the Anticancer Drug Bleomycin. Cancer Res 64: 1102–1109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

