Aromatic-aromatic interactions: analysis of π-π interactions in interleukins and TNF proteins
- PMID: 23750094
- PMCID: PMC3670127
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630009432
Aromatic-aromatic interactions: analysis of π-π interactions in interleukins and TNF proteins
Abstract
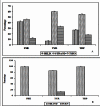
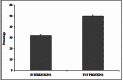
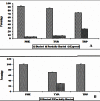
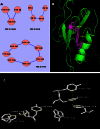
Aromatic-aromatic hydrogen bonds are important in many areas of chemistry, biology and materials science. In this study we have analyzed the roles played by the π-π interactions in interleukins (ILs) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) proteins. Majority of π-π interacting residues are conserved in ILs and TNF proteins. The accessible surface area calculations in these proteins reveal that these interactions might be important in stabilizing the inner core regions of these proteins. In addition to π-π interactions, the aromatic residues also form π-networks in ILs and TNF proteins. The results obtained in the present study indicate that π-π interactions and π-π networks play important roles in the structural stability of ILs and TNF proteins.
Keywords: ILs; TNF proteins; stability; structure; π-network; π-π interactions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Computation of non-covalent interactions in TNF proteins and interleukins.Cytokine. 2006 Sep;35(5-6):263-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2006.09.005. Epub 2006 Oct 18. Cytokine. 2006. PMID: 17055289
-
Influence of C-H...pi hydrogen bonds in interleukins.In Silico Biol. 2008;8(3-4):261-73. In Silico Biol. 2008. PMID: 19032161
-
π-π Interactions in structural stability: role in RNA binding proteins.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(3):853-63. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9573-0. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23526191
-
[Noncovalent cation-π interactions--their role in nature].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Nov 7;68:1276-86. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1127950. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 25380210 Review. Polish.
-
Principles of Cation-π Interactions for Engineering Mussel-Inspired Functional Materials.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Apr 19;55(8):1171-1182. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00068. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 35344662 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet integrin αIIbβ3 plays a key role in a venous thrombogenesis mouse model.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 4;15(1):8612. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52869-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39366965 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
