Exosomes go with the Wnt
- PMID: 23739155
- PMCID: PMC3498077
- DOI: 10.4161/cl.21981
Exosomes go with the Wnt
Abstract
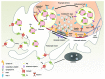
Exosomes, small secreted microvesicles, are implicated in intercellular communication in diverse cell types, transporting protein, lipid and nucleic acid cargo that impact the physiology of recipient cells. Besides the signaling function of exosomes they also serve as a mechanism to dispose obsolete cellular material.1 Particularly exciting is the involvement of exosomal communication in the nervous system, as this has important implications for brain development and function. The properties of exosomes are also beginning to entice the biomedical community since they represent potentially novel avenues for the targeted delivery of customized exosome cargo, such as miRNAs, during disease. Our findings implicating exosomes in trans-synaptic communication emerged from the serendipitous observation that at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction (NMJ) the release of a signaling molecule, Wnt1/Wingless (Wg) and its binding partner Evenness Interrupted (Evi)/Wntless (Wls)/Sprint (Srt), were released by motorneurons in association with vesicles, which we postulated to be exosomes.2 In our most recent paper3 using in vivo analysis at the Drosophila NMJ as well as in cultured insect cells we formally demonstrate that Evi rides in exosomes that are released to the extracellular space and identify some of the players involved in their release. In addition, a proteomic analysis of exosomes highlights novel potential function of exosomes.
Keywords: Drosophila; Evi/Wntless/GPR177/mig-14; RNA-binding proteins; Rab11; Syntaxin 1A; Wingless; Wnt; exosomal proteome; exosome release; local translation; neuromuscular junction; retromer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16820-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.342667. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22437826 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless.Cell. 2009 Oct 16;139(2):393-404. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.051. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19837038 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila S2 cells secrete wingless on exosome-like vesicles but the wingless gradient forms independently of exosomes.Traffic. 2013 Jan;14(1):82-96. doi: 10.1111/tra.12016. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 23035643 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer's disease.J Neurovirol. 2019 Oct;25(5):702-709. doi: 10.1007/s13365-018-0695-4. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Neurovirol. 2019. PMID: 30610738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Evi/Wntless in exporting Wnt proteins.Development. 2023 Feb 15;150(3):dev201352. doi: 10.1242/dev.201352. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Development. 2023. PMID: 36763105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions.J Extracell Vesicles. 2015 May 14;4:27066. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.27066. eCollection 2015. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015. PMID: 25979354 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles: clinical promise and open questions.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:439-464. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124630. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25292428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal Wnt7a from a low metastatic subclone promotes lung metastasis of a highly metastatic subclone in the murine 4t1 breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2022 Sep 12;24(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01557-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36096830 Free PMC article.
-
Transsynaptic modality codes in the brain: possible involvement of synchronized spike timing, microRNAs, exosomes and epigenetic processes.Front Integr Neurosci. 2013 Jan 4;6:126. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2012.00126. eCollection 2012. Front Integr Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23316146 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome Biogenesis, Regulation, and Function in Viral Infection.Viruses. 2015 Sep 17;7(9):5066-83. doi: 10.3390/v7092862. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26393640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
