A stress-activated, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-ATF/CREB pathway regulates posttranscriptional, sequence-dependent decay of target RNAs
- PMID: 23732911
- PMCID: PMC3719685
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00349-13
A stress-activated, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-ATF/CREB pathway regulates posttranscriptional, sequence-dependent decay of target RNAs
Abstract
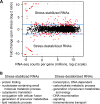
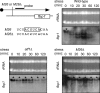
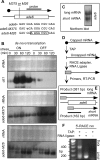
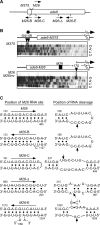
Broadly conserved, mitogen-activated/stress-activated protein kinases (MAPK/SAPK) of the p38 family regulate multiple cellular processes. They transduce signals via dimeric, basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors of the ATF/CREB family (such as Atf2, Fos, and Jun) to regulate the transcription of target genes. We report additional mechanisms for gene regulation by such pathways exerted through RNA stability controls. The Spc1 (Sty1/Phh1) kinase-regulated Atf1-Pcr1 (Mts1-Mts2) heterodimer of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe controls the stress-induced, posttranscriptional stability and decay of sets of target RNAs. Whole transcriptome RNA sequencing data revealed that decay is associated nonrandomly with transcripts that contain an M26 sequence motif. Moreover, the ablation of an M26 sequence motif in a target mRNA is sufficient to block its stress-induced loss. Conversely, engineered M26 motifs can render a stable mRNA into one that is targeted for decay. This stress-activated RNA decay (SARD) provides a mechanism for reducing the expression of target genes without shutting off transcription itself. Thus, a single p38-ATF/CREB signal transduction pathway can coordinately induce (promote transcription and RNA stability) and repress (promote RNA decay) transcript levels for distinct sets of genes, as is required for developmental decisions in response to stress and other stimuli.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation-independent regulation of Atf1-promoted meiotic recombination by stress-activated, p38 kinase Spc1 of fission yeast.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005533. Epub 2009 May 14. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19436749 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Atf1 protein levels by Sty1-mediated phosphorylation and heterodimerization with Pcr1.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5160-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608526200. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17182615
-
Distinct regions of ATF/CREB proteins Atf1 and Pcr1 control recombination hotspot ade6-M26 and the osmotic stress response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 May;36(9):2838-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn037. Epub 2008 Mar 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18375981 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-mimicking Atf1 mutants bypass the transcription activating function of the MAP kinase Sty1 of fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):97-102. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0730-7. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28799013 Review.
-
Nuclear roles and regulation of chromatin structure by the stress-dependent MAP kinase Sty1 of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Nov;82(3):542-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07851.x. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21992435 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Forward Genetics: Population-Scale Analyses of Allele Replacements Spanning Thousands of Base Pairs in Fission Yeast.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Dec 3;9(12):4097-4106. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400805. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 31597677 Free PMC article.
-
Nonsense codon suppression in fission yeast due to mutations of tRNA(Ser.11) and translation release factor Sup35 (eRF3).Curr Genet. 2015 May;61(2):165-73. doi: 10.1007/s00294-014-0465-7. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Curr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25519804 Free PMC article.
-
Gcn2 eIF2α kinase mediates combinatorial translational regulation through nucleotide motifs and uORFs in target mRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 18;48(16):8977-8992. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa608. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32710633 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of bZIP Atf1ortholog global regulators in fungi.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Aug;105(14-15):5769-5783. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11431-7. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34302199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H3S28 phosphorylation is a hallmark of the transcriptional response to cellular stress.Genome Res. 2014 Nov;24(11):1808-20. doi: 10.1101/gr.176255.114. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 25135956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanso M, Vargas-Perez I, Garcia P, Ayte J, Hidalgo E. 2011. Nuclear roles and regulation of chromatin structure by the stress-dependent MAP kinase Sty1 of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol. Microbiol. 82:542–554 - PubMed
-
- Shiozaki K, Russell P. 1996. Conjugation, meiosis, and the osmotic stress response are regulated by Spc1 kinase through Atf1 transcription factor in fission yeast. Genes Dev. 10:2276–2288 - PubMed
-
- Shiozaki K, Russell P. 1995. Cell-cycle control linked to extracellular environment by MAP kinase pathway in fission yeast. Nature 378:739–743 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
