Targeted drug delivery and cross-linking induced apoptosis with anti-CD37 based dual-ligand immunoliposomes in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
- PMID: 23726226
- PMCID: PMC3756150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.04.063
Targeted drug delivery and cross-linking induced apoptosis with anti-CD37 based dual-ligand immunoliposomes in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
Abstract
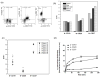
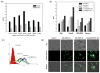
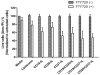
Despite advances in chemo and immunotherapeutic agents for B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), the undesirable adverse side effects due to non-specific cellular uptake remain to be addressed. We identified anti-CD37 monoclonal antibody immunoliposomes (ILs) as vehicles for targeted delivery to B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. To achieve maximal benefits for all patients, a new strategy of dual-ligand immunoliposomes (dILs) was developed. A combinatorial antibody microarray technology was adapted to quickly identify optimal antibody combinations for individual patient cells. For proof-of-concept, a B-cell specific antibody, either anti-CD19 or anti-CD20, was combined with anti-CD37 to construct dILs with enhanced selectivity and efficacy. Consistent with data from the antibody microarray, these dILs provided highly specific targeting to both leukemia cell lines and B-CLL patient cells. Compared with the single antibody ILs, the anti-CD19/CD37 dILs clearly demonstrated superior delivery efficiency and apoptosis induction to B-CLL patient cells, whereas the anti-CD20/anti-CD37 dILs were found to be the most efficient for delivery to leukemia cell lines. In addition, it was observed that anti-CD37 ILs without payload drug mediated effective CD37 cross-linking and induced potent apoptosis induction. The anti-CD19/CD20 dILs showed the improved cell apoptosis induction compared to either anti-CD19 ILs or anti-CD20 ILs. Our findings suggest that the dual-ligand ILs may provide a preferred strategy of personalized nanomedicine for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.
Copyright © 2013. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel anti-CD37 antibody-drug conjugate with multiple anti-tumor mechanisms for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.Blood. 2013 Nov 14;122(20):3500-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-505685. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24002446
-
Current and emerging monoclonal antibody treatments for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: state of the art.Expert Rev Hematol. 2014 Dec;7(6):841-57. doi: 10.1586/17474086.2014.963048. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Expert Rev Hematol. 2014. PMID: 25249370 Review.
-
Pro-apoptotic effect of an anti-CD37 scFv-Fc fusion protein, in combination with the anti-CD20 antibody, ofatumumab, on tumour cells from B-cell malignancies.Eur J Cancer. 2014 Oct;50(15):2677-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.07.021. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Eur J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25154027
-
Emerging monoclonal antibodies and related agents for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Future Oncol. 2013 Jan;9(1):69-91. doi: 10.2217/fon.12.157. Future Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23252565 Review.
-
The CD37-targeted antibody-drug conjugate IMGN529 is highly active against human CLL and in a novel CD37 transgenic murine leukemia model.Leukemia. 2014 Jul;28(7):1501-10. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.32. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Leukemia. 2014. PMID: 24445867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-CD37 chimeric antigen receptor T cells are active against B- and T-cell lymphomas.Blood. 2018 Oct 4;132(14):1495-1506. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-04-842708. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30089630 Free PMC article.
-
Recent strategies towards the surface modification of liposomes: an innovative approach for different clinical applications.3 Biotech. 2020 Apr;10(4):163. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-2144-3. Epub 2020 Mar 10. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 32206497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetraspanins as therapeutic targets in hematological malignancy: a concise review.Front Physiol. 2015 Mar 23;6:91. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00091. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25852576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor antigen ROR1 targeted drug delivery mediated selective leukemic but not normal B-cell cytotoxicity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leukemia. 2015 Feb;29(2):346-55. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.199. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 24947019 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Nanosystems.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Jun 21;6(17):1900101. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900101. eCollection 2019 Sep 4. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31508270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tam CS, Keating MJ. Chemoimmunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7(9):521–532. - PubMed
-
- Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(8):804–815. - PubMed
-
- Pleyer L, Egle A, Hartmann TN, Greil R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of CLL: novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6(7):405–418. - PubMed
-
- Jaglowski SM, Byrd JC. Rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Hematol. 2010;47(2):156–169. - PubMed
-
- Osterborg A, Fassas AS, Anagnostopoulos A, Dyer MJ, Catovsky D, Mellstedt H. Humanized CD52 monoclonal antibody Campath-1H as first-line treatment in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1996;93(1):151–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

