Synaptic Zn2+ inhibits neurotransmitter release by promoting endocannabinoid synthesis
- PMID: 23719795
- PMCID: PMC3733213
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0237-13.2013
Synaptic Zn2+ inhibits neurotransmitter release by promoting endocannabinoid synthesis
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2014 May 21;34(21):7394
Abstract
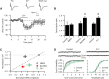
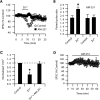
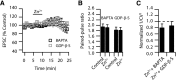
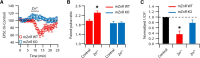
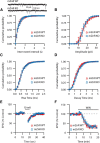
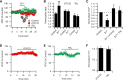
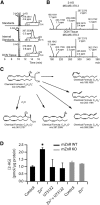
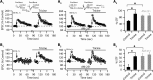
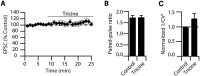
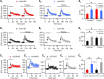
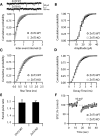
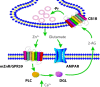
Although it is well established that many glutamatergic neurons sequester Zn(2+) within their synaptic vesicles, the physiological significance of synaptic Zn(2+) remains poorly understood. In experiments performed in a Zn(2+)-enriched auditory brainstem nucleus--the dorsal cochlear nucleus--we discovered that synaptic Zn(2+) and GPR39, a putative metabotropic Zn(2+)-sensing receptor (mZnR), are necessary for triggering the synthesis of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). The postsynaptic production of 2-AG, in turn, inhibits presynaptic probability of neurotransmitter release, thus shaping synaptic strength and short-term synaptic plasticity. Zn(2+)-induced inhibition of transmitter release is absent in mutant mice that lack either vesicular Zn(2+) or the mZnR. Moreover, mass spectrometry measurements of 2-AG levels reveal that Zn(2+)-mediated initiation of 2-AG synthesis is absent in mice lacking the mZnR. We reveal a previously unknown action of synaptic Zn(2+): synaptic Zn(2+) inhibits glutamate release by promoting 2-AG synthesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol inhibits long-term potentiation of glutamatergic synapses onto ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons in mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 May;33(10):1751-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07648.x. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21410793
-
Endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde modulation of synaptic transmission.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014 Dec;29:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24747340 Review.
-
Synaptically driven endocannabinoid release requires Ca2+-assisted metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 to phospholipase Cbeta4 signaling cascade in the cerebellum.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 20;25(29):6826-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0945-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16033892 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the sites of 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis and action imply retrograde endocannabinoid signaling at both GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses in the ventral tegmental area.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Jan;54(1):95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.05.028. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 17655884 Free PMC article.
-
The serine hydrolases MAGL, ABHD6 and ABHD12 as guardians of 2-arachidonoylglycerol signalling through cannabinoid receptors.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Feb;204(2):267-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02280.x. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 21418147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Does Short-Term Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Influence Brain Hippocampus Gene Expression of Zinc Transporter-3?Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 13;16(7):15800-10. doi: 10.3390/ijms160715800. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26184176 Free PMC article.
-
The Zinc Sensing Receptor, ZnR/GPR39, in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 1;19(2):439. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020439. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29389900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of GPR39 in Neurovascular Homeostasis and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 30;22(15):8200. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158200. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-specific gain modulation by synaptically released zinc in cortical circuits of audition.Elife. 2017 Sep 9;6:e29893. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29893. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28887876 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc as a Neuromodulator in the Central Nervous System with a Focus on the Olfactory Bulb.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Sep 21;11:297. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00297. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29033788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS043277/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AT006822/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS043277/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072506/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC007905/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- HL64937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32DC011664/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DK072506/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DC011664/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL103455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL058115/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL058115/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT006822/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL103455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS043277/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL058115/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DC007905/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
