Interferon-α sensitizes HBx-expressing hepatocarcinoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs through inhibition of HBx-mediated NF-κB activation
- PMID: 23718853
- PMCID: PMC3680016
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-168
Interferon-α sensitizes HBx-expressing hepatocarcinoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs through inhibition of HBx-mediated NF-κB activation
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is characterized by high chemotherapy resistance; however, the underlying mechanism has not been fully clarified. In addition, HBx protein has been reported to play a key role in virus-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis. Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the role of HBx in the drug-resistance of HBV-related HCC and examine whether such drug-resistance can be reversed by IFN-α treatment.
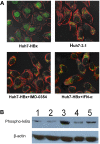
Methods: We established HBx-expressing cells by liposome-mediated transfection of HBx into the Huh7 cell line. MTT, Annexin V/PI, and cell cycle assay were used for determining the cellular growth inhibition, apoptosis, and growth arrest, respectively, after treatment with chemical drug. We further used tumor-bearing mice model to compare the tumor growth inhibition efficacy of ADM and 5-FU between the Huh7-HBx group and the control group, as well as the ADM + IFN-α or ADM + IMD treated group and the ADM treated group. SQ-Real time-PCR was performed to analyze the expression of MDR-associated genes and anti-apoptotic genes. Moreover, immunofluorescence and Western blotting were used to determine the subcellular localization of p65 and the phosphorylation of IκBα.
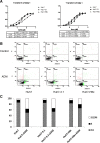
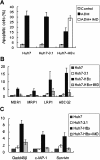
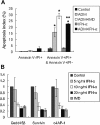
Results: The IC₅₀ values of Huh7-HBx cells against ADM and Amn were 2.317 and 1.828-folds higher than those of Huh7-3.1 cells, respectively. The apoptosis ratio and growth arrest was significantly lower in Huh7-HBx cells after treatment with ADM. The in vivo experiment also confirmed that the Huh7-HBx group was much more resistant to ADM or 5-FU than the control. Furthermore, the expression of MDR-associated genes, such as MDR1, MRP1, LRP1, and ABCG2, were significantly up-regulated in Huh7-HBx cells, and the NF-κB pathway was activated after HBx gene transfection in Huh7 cells. However, combined with IFN-α in ADM treatment, the HBx induced drug-resistance in Huh7-HBx cells can be partly abolished in in vitro and in vivo models. Moreover, we found that the NF-κB canonical pathway was affected by IFN-α treatment, and the expression of anti-apoptotic genes, such as Gadd45β, Survivin, and c-IAP-1 was down-regulated by IFN-α treatment in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusions: HBx protein can induce MDR of HBV-related HCC by activating the NF-κB pathway, which can be partly abolished by IFN-α treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of the NF-κB pathway in multidrug resistance induced by HBx in a hepatoma cell line.J Viral Hepat. 2011 Oct;18(10):e439-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01463.x. Epub 2011 May 27. J Viral Hepat. 2011. PMID: 21914061
-
HDM2 Promotes NEDDylation of Hepatitis B Virus HBx To Enhance Its Stability and Function.J Virol. 2017 Jul 27;91(16):e00340-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00340-17. Print 2017 Aug 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28592528 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-alpha restrains growth and invasive potential of hepatocellular carcinoma induced by hepatitis B virus X protein.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Sep 28;14(36):5564-9; discussion 5568. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5564. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18810776 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-HBV drugs suppress the growth of HBV-related hepatoma cells via down-regulation of hepatitis B virus X protein.Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 28;392:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28192212
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes UV-induced apoptosis by transcriptional transactivation of Fas ligand gene expression.IUBMB Life. 2005 Sep;57(9):651-8. doi: 10.1080/15216540500239697. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16203685 Review.
Cited by
-
ISG15 in the tumorigenesis and treatment of cancer: An emerging role in malignancies of the digestive system.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):74393-74409. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11911. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in hepatoma cells.J Transl Med. 2016 May 5;14(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0888-7. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27150195 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells Modulates Resistance to Cisplatin in the A549/DDP Cell Line.J Cancer. 2017 Sep 16;8(16):3287-3295. doi: 10.7150/jca.19426. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29158802 Free PMC article.
-
HBx interacted with Smad4 to deprive activin a growth inhibition function in hepatocyte HL7702 on CRM1 manner.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):3405-15. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4076-9. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26449823
-
Hepatitis C Virus-Induced FUT8 Causes 5-FU Drug Resistance in Human Hepatoma Huh7.5.1 Cells.Viruses. 2019 Apr 24;11(4):378. doi: 10.3390/v11040378. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31022917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nerenstone SR, Ihde DC, Friedman MA. Clinical trials in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future directions. Cancer Treat Rev. 1988;15:1–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

