Prenylation and membrane localization of Cdc42 are essential for activation by DOCK7
- PMID: 23718289
- PMCID: PMC3752685
- DOI: 10.1021/bi301688g
Prenylation and membrane localization of Cdc42 are essential for activation by DOCK7
Abstract
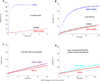
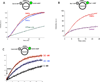
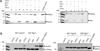
The unconventional guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) family comprising 11 DOCK180 related proteins is classified into four subfamilies, A through D, based on their relative GEF activity toward the closely related Rac and Cdc42 GTPases. DOCK proteins participate in the remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton and are key regulators of cell motility, phagocytosis, and adhesion. Here we show that the guanine nucleotide exchange domain of DOCK7, DHR2 (for DOCK homology region 2), is a potent GEF for prenylated Cdc42 and Rac1 in a model liposome system, demonstrating that the prenylation and membrane localization of Cdc42 or Rac1 are necessary for their activation by DOCK7. Additionally, we identify DOCK7 residues that confer GTPase GEF specificity. Finally, using our liposome reconstitution assay, we show that a more narrowly defined GEF domain of DHR2 (designated DHR2s) harbors an N-terminal site distinct from the GEF active site that binds preferentially to the active, GTP-bound forms of Cdc42 and Rac1 and thereby recruits free DHR2s from solution to the membrane surface. This recruitment results in a progressive increase in the effective concentration of DHR2s at the membrane surface that in turn provides for an accelerated rate of guanine nucleotide exchange on Cdc42. The positive cooperativity observed in our reconstituted system suggests that the action of DOCK7 in vivo may involve the coordinated integration of Cdc42/Rac signaling in the context of the membrane recruitment of a DOCK7 GEF complex.
Figures

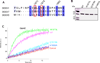

Similar articles
-
Structural Basis for the Dual Substrate Specificity of DOCK7 Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor.Structure. 2019 May 7;27(5):741-748.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Structure. 2019. PMID: 30853411
-
Multiple factors confer specific Cdc42 and Rac protein activation by dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK) nucleotide exchange factors.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):25341-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.236455. Epub 2011 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21613211 Free PMC article.
-
Dock6, a Dock-C subfamily guanine nucleotide exchanger, has the dual specificity for Rac1 and Cdc42 and regulates neurite outgrowth.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Feb 15;313(4):791-804. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.11.017. Epub 2006 Dec 6. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17196961
-
Structural biology of DOCK-family guanine nucleotide exchange factors.FEBS Lett. 2023 Mar;597(6):794-810. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14523. Epub 2022 Nov 4. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36271211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous mutation of Dock7 results in lower trabecular bone mass and impaired periosteal expansion in aged female Misty mice.Bone. 2017 Dec;105:103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28821457 Free PMC article.
-
Small-GTPase-associated signaling by the guanine nucleotide exchange factors CpDock180 and CpCdc24, the GTPase effector CpSte20, and the scaffold protein CpBem1 in Claviceps purpurea.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Apr;13(4):470-82. doi: 10.1128/EC.00332-13. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24489041 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Cdc42 is necessary for sustained oscillations of Ca2+ and PIP2 stimulated by antigen in RBL mast cells.Biol Open. 2014 Jul 4;3(8):700-10. doi: 10.1242/bio.20148862. Biol Open. 2014. PMID: 24996924 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts (RAGE): A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective.J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 14;60(17):7213-7232. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00058. Epub 2017 May 19. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28482155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin cytoskeleton dynamics in stem cells from autistic individuals.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 24;8(1):11138. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29309-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30042445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cerione RA. Cdc42: new roads to travel. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:127–132. - PubMed
-
- Chardin P. The ras superfamily proteins. Biochimie. 1998;70:865–868. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL, Diekmann D, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992;70:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Tapon N, Hall A. Rho, Rac and Cdc42 GTPases regulate the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997;9:86–92. - PubMed
-
- Williams CL. The polybasic region of Ras and Rho family small GTPases: a regulator of protein interactions and membrane association and a site of nuclear localization signal sequences. Cell. Signal. 2003;15:1071–1080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

