Pirin is an iron-dependent redox regulator of NF-κB
- PMID: 23716661
- PMCID: PMC3683729
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1221743110
Pirin is an iron-dependent redox regulator of NF-κB
Abstract
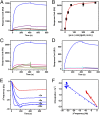
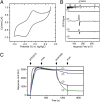
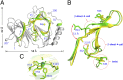
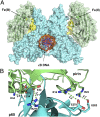
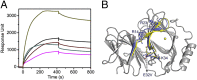
Pirin is a nuclear nonheme Fe protein of unknown function present in all human tissues. Here we describe that pirin may act as a redox sensor for the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) transcription factor, a critical mediator of intracellular signaling that has been linked to cellular responses to proinflammatory signals and controls the expression of a vast array of genes involved in immune and stress responses. Pirin's regulatory effect was tested with several metals and at different oxidations states, and our spectroscopic results show that only the ferric form of pirin substantially facilitates binding of NF-κB proteins to target κB genes, a finding that suggests that pirin performs a redox-sensing role in NF-κB regulation. The molecular mechanism of such a metal identity- and redox state-dependent regulation is revealed by our structural studies of pirin. The ferrous and ferric pirin proteins differ only by one electron, yet they have distinct conformations. The Fe center is shown to play an allosteric role on an R-shaped surface area that has two distinct conformations based on the identity and the formal redox state of the metal. We show that the R-shaped area composes the interface for pirin-NF-κB binding that is responsible for modulation of NF-κB's DNA-binding properties. The nonheme Fe protein pirin is proposed to serve as a reversible functional switch that enables NF-κB to respond to changes in the redox levels of the cell nucleus.
Keywords: coregulator; metalloprotein; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species (ROS); signal transduction activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
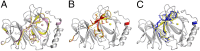

Similar articles
-
Redox-Specific Allosteric Modulation of the Conformational Dynamics of κB DNA by Pirin in the NF-κB Supramolecular Complex.Biochemistry. 2017 Sep 19;56(37):5002-5010. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00528. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28825294
-
Crystal structure of human pirin: an iron-binding nuclear protein and transcription cofactor.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 9;279(2):1491-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310022200. Epub 2003 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14573596
-
Fe(II)/Fe(III) Redox Process Can Significantly Modulate the Conformational Dynamics and Electrostatics of Pirin in NF-κB Regulation.ACS Omega. 2016 Nov 7;1(5):837-842. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00231. eCollection 2016 Nov 30. ACS Omega. 2016. PMID: 31457166 Free PMC article.
-
Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005 Mar-Apr;7(3-4):395-403. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.395. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005. PMID: 15706086 Review.
-
Multiple redox regulation in NF-kappaB transcription factor activation.Biol Chem. 1997 Nov;378(11):1237-45. Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9426183 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of full flavor and denicotinized cigarettes exposure on the brain microvascular endothelium: a microarray-based gene expression study using a human immortalized BBB endothelial cell line.BMC Neurosci. 2015 Jun 23;16:38. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0173-3. BMC Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26099276 Free PMC article.
-
New functions of pirin proteins and a 2-ketoglutarate: Ferredoxin oxidoreductase ortholog in Bacteroides fragilis metabolism and their impact on antimicrobial susceptibility to metronidazole and amixicile.Microbiologyopen. 2024 Aug;13(4):e1429. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1429. Microbiologyopen. 2024. PMID: 39109824 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating radiosensitive genes improves prediction of radiosensitivity or radioresistance in patients with oesophageal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jun;17(6):5377-5388. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10240. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31186755 Free PMC article.
-
PIRIN2 stabilizes cysteine protease XCP2 and increases susceptibility to the vascular pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2014 Sep;79(6):1009-19. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12602. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24947605 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Pirin, an Oxidative Stress Sensor Protein, in Epithelial Carcinogenesis.Biology (Basel). 2021 Feb 4;10(2):116. doi: 10.3390/biology10020116. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33557375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46(5):705–716. - PubMed
-
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Inducibility of κ immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-κB by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986;47(6):921–928. - PubMed
-
- Romashkova JA, Makarov SS. NF-κB is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signalling. Nature. 1999;401(6748):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Lin A. NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(3):221–227. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Verma IM. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(10):725–734. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

