Modulation of the CXC chemokine receptor 4 agonist activity of ubiquitin through C-terminal protein modification
- PMID: 23697661
- PMCID: PMC4113718
- DOI: 10.1021/bi400254f
Modulation of the CXC chemokine receptor 4 agonist activity of ubiquitin through C-terminal protein modification
Abstract
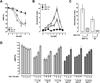
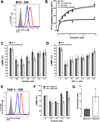
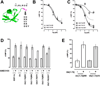
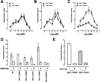
Extracellular ubiquitin has recently been described as a CXC chemokine receptor (CXCR) 4 agonist. Studies on the structure-function relationship suggested that the C-terminus of ubiquitin facilitates CXCR4 activation. It remains unknown, however, whether C-terminal processing of ubiquitin could be biologically relevant and whether modifications of the ubiquitin C-terminus can modulate CXCR4 activation. We show that C-terminal truncated ubiquitin antagonizes ubiquitin and stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α induced effects on cell signaling and function. Reduction of cell surface expression of insulin degrading enzyme (IDE), which cleaves the C-terminal di-Gly of ubiquitin, enhances ubiquitin induced reduction of cAMP levels in BV2 and THP-1 cells, but does not influence changes in cAMP levels in response to SDF-1α. Reduction of cell surface IDE expression in THP-1 cells also increases the chemotactic activity of ubiquitin. As compared with native ubiquitin, C-terminal Tyr extension of ubiquitin results in reduced CXCR4 mediated effects on cellular cAMP levels and abolishes chemotactic activity. Replacement of C-terminal di-Gly of ubiquitin with di-Val or di-Arg enhances CXCR4 mediated effects on cAMP levels and the di-Arg substitution exerts increased chemotactic activity, when compared with wild type ubiquitin. The chemotactic activities of the di-Val and di-Arg mutants and their effects on cAMP levels can be antagonized with C-terminal truncated ubiquitin. These data suggest that the development of CXCR4 ligands with enhanced agonist activities is possible and that C-terminal processing of ubiquitin could constitute a biological mechanism, which regulates termination of receptor signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CXC chemokine receptor 4 signaling upon co-activation with stromal cell-derived factor-1α and ubiquitin.Cytokine. 2014 Feb;65(2):121-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24373940 Free PMC article.
-
The CXC chemokine receptor 4 ligands ubiquitin and stromal cell-derived factor-1α function through distinct receptor interactions.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 23;286(38):33466-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.233742. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21757744 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of ubiquitin-CXC chemokine receptor 4 interaction.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 23;286(51):44145-44152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.298505. Epub 2011 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22039044 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 and cAMP induce stromal cell-derived factor-1 chemotaxis in astroglia by up-regulating CXCR4 cell surface expression. Implications for brain inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 18;277(42):39801-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200472200. Epub 2002 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12171912
-
CXCL14 antagonizes the CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling axis.Biomol Concepts. 2014 May;5(2):167-73. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2014-0007. Biomol Concepts. 2014. PMID: 25372750 Review.
Cited by
-
CXC chemokine receptor 4 signaling upon co-activation with stromal cell-derived factor-1α and ubiquitin.Cytokine. 2014 Feb;65(2):121-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24373940 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular ubiquitin increases expression of angiogenic molecules and stimulates angiogenesis in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells.Microcirculation. 2014 May;21(4):324-32. doi: 10.1111/micc.12109. Microcirculation. 2014. PMID: 24308702 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4: From Signaling to Clinical Applications in Neuroendocrine Neoplasms.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 8;16(10):1799. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101799. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective Potential of Exogenous Ubiquitin.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021 Dec;35(6):1227-1232. doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07042-5. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021. PMID: 32910339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into Mechanisms and Functions of Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Receptor 4 Heteromerization in Vascular Smooth Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 20;17(5):971. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060971. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27331810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Majetschak M. Extracellular ubiquitin: immune modulator and endogenous opponent of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011;89:205–219. - PubMed
-
- Majetschak M, Krehmeier U, Bardenheuer M, Denz C, Quintel M, Voggenreiter G, Obertacke U. Extracellular ubiquitin inhibits the TNF-alpha response to endotoxin in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and regulates endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in critical illness. Blood. 2003;101:1882–1890. - PubMed
-
- Earle SA, El-Haddad A, Patel MB, Ruiz P, Pham SM, Majetschak M. Prolongation of skin graft survival by exogenous ubiquitin. Transplantation. 2006;82:1544–1546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

