Regulation of stem cell populations by microRNAs
- PMID: 23696365
- PMCID: PMC3901537
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-6621-1_18
Regulation of stem cell populations by microRNAs
Abstract
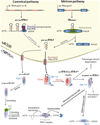
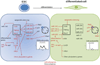
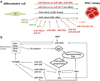
miRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that have emerged as crucial post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression. They are key players in various critical cellular processes such as proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis and differentiation. Self-renewal capacity and differentiation potential are hallmarks of stem cells. The switch between self-renewal and differentiation requires rapid widespread changes in gene expression. Since miRNAs can repress the translation of many mRNA targets, they are good candidates to regulate cell fates. In the past few years, miRNAs have appeared as important new actors in stem cell development by regulating differentiation and maintenance of stem cells. In this chapter we will focus on the role of miRNAs in various stem cell populations. After an introduction on microRNA biogenesis, we will review the recent knowledge on miRNA expression and function in pluripotent cells and during the acquisition of stem cell fate. We will then briefly examine the role of miRNAs in adult and cancer stem cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miRNAs highlights in stem and cancer cells.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011 Nov;11(13):1165-82. doi: 10.2174/138955711797655371. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22353225 Review.
-
[The effect of microRNAs on the regulatory network of pluripotency in embryonic stem cells].Yi Chuan. 2013 Oct;35(10):1153-66. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2013.01153. Yi Chuan. 2013. PMID: 24459889 Review. Chinese.
-
The Key Role of MicroRNAs in Self-Renewal and Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6285. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176285. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32877989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression and Functional Roles of miRNAs in Embryonic and Lineage-Specific Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(3):278-289. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190123162402. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30674265 Review.
-
The stem cell state.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;786:1-4. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-6621-1_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23696348
Cited by
-
Down-Regulation of miR-146a Expression Induces Allergic Conjunctivitis in Mice by Increasing TSLP Level.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jul 11;21:2000-7. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894563. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26166175 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular small non-coding RNA contaminants in fetal bovine serum and serum-free media.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 2;9(1):5538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41772-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30940830 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury and enhance reconditioning of donor lungs after circulatory death.Respir Res. 2017 Dec 21;18(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0704-9. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 29268735 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipid-mediated inflammatory signaling leading to autophagy inhibition converts erythropoiesis to myelopoiesis in human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Sep;26(9):1796-1812. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0245-x. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30546074 Free PMC article.
-
Polysome profiling shows the identity of human adipose-derived stromal/stem cells in detail and clearly distinguishes them from dermal fibroblasts.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Nov 15;23(22):2791-802. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0496. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 25068904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

