The key gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is secreted during prolonged glucose starvation and is internalized following glucose re-feeding via the non-classical secretory and internalizing pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 23673352
- PMCID: PMC3999075
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.24936
The key gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is secreted during prolonged glucose starvation and is internalized following glucose re-feeding via the non-classical secretory and internalizing pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
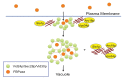
In Saccharomyces cerevisia, the key gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is secreted into the periplasm during prolonged glucose starvation and is internalized into Vid/endosomes following glucose re-feeding. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase does not contain signal sequences required for the classical secretory and endocytic pathways. Hence, the secretion and internalization are mediated via the non-classical pathways.
Keywords: PI3K; fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase; gluconeogenesis; non-classical secretion and endocytosis; vacuole import and degradation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vps34p is required for the decline of extracellular fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in the vacuole import and degradation pathway.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 21;287(39):33080-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.360412. Epub 2012 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22833678 Free PMC article.
-
The vacuolar import and degradation pathway merges with the endocytic pathway to deliver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase to the vacuole for degradation.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 19;283(38):26116-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709922200. Epub 2008 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18660504 Free PMC article.
-
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, Malate Dehydrogenase, Isocitrate Lyase, Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase, and Cyclophilin A are secreted in Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in low glucose.Commun Integr Biol. 2013 Nov 1;6(6):e27216. doi: 10.4161/cib.27216. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Commun Integr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24563717 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytosis and Endocytosis of Small Vesicles across the Plasma Membrane in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Membranes (Basel). 2014 Sep 3;4(3):608-29. doi: 10.3390/membranes4030608. Membranes (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25192542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Functioning of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase--main enzyme of gluconeogenesis in microorganisms].Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2002 Jul-Aug;74(4):24-32. Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2002. PMID: 14964858 Review. Ukrainian.
Cited by
-
Comparative proteomic analysis of Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri periplasmic proteins reveals changes in cellular envelope metabolism during in vitro pathogenicity induction.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Jan;19(1):143-157. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12507. Epub 2017 Feb 5. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 27798950 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Proteins Secreted from the Oryza meyeriana Suspension-Cultured Cells Induced by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.PLoS One. 2016 May 19;11(5):e0154793. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154793. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27196123 Free PMC article.
-
The endocytosis gene END3 is essential for the glucose-induced rapid decline of small vesicles in the extracellular fraction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Extracell Vesicles. 2014 Mar 21;3. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.23497. eCollection 2014. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014. PMID: 24665361 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signalling pathway regulation by RanBPM: molecular insights and disease implications.Open Biol. 2017 Jun;7(6):170081. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170081. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28659384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and Functional Insights into GID/CTLH E3 Ligase Complexes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 24;23(11):5863. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115863. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mijaljica D, Prescott M, Klionsky DJ, Devenish RJ. Autophagy and vacuole homeostasis: a case for self-degradation? Autophagy. 2007;3:417–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
