Clinical implication of Time To Brain Metastasis (TTBM) according to breast cancer subtypes
- PMID: 23667803
- PMCID: PMC3647103
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-136
Clinical implication of Time To Brain Metastasis (TTBM) according to breast cancer subtypes
Abstract
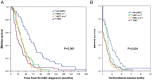
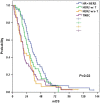
The aims of the present study were to investigate how breast cancer (BC) subtypes and treatment affect time to brain metastasis (TTBM). We retrospectively investigated 189 consecutive patients who were diagnosed with brain metastasis (BM) from BC between 2000 and 2009 at Samsung Medical Center. We analyzed TTBM from initial diagnosis of metastatic BC according to subtypes and trastzumab (T) administration before BM diagnosis. The median age of 189 BM patients from BC was 48 years. We divided TTBM into four groups considering BC subtypes and treatment; HR-positive/HER2-negative (n=45), HER2-positive with T before BM development (n=47), HER2-positive without T before BM development (n=39), and TNBC (n=58). The median TTBMs for each group were 17.5 months, 13.7 months, 5.8 months, and 2.9 months, respectively (p<0.001). HER2-positive without T (HR 1.892, p=0.008) and TNBC (HR 1.652, p=0.023) were independently associated with shorter TTBM. In multivariate analysis, HER2-positive without T (hazard ratio 1.725, p=0.002) and TNBC (hazard ratio 1.579, p=0.022) were independent risk factors for worse metastatic OS compared with HR-positive/HER2-negative subtype. TTBMs were shorter in patients with HER2-positive without T and TNBC among BC subtypes. Prospective clinical study for high risk patients for early BM is warranted.
Keywords: Brain metastases; Breast cancer; HER2; Trastuzumab; Triple negative.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic factors of brain metastasis and survival among HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients: a systematic literature review.BMC Cancer. 2021 Aug 28;21(1):967. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08708-5. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34454469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New brain metastases after whole-brain radiotherapy of initial brain metastases in breast cancer patients: the significance of molecular subtypes (KROG 16-12).Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Apr;186(2):453-462. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-06043-0. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33392845
-
The prognostic contribution of clinical breast cancer subtype, age, and race among patients with breast cancer brain metastases.Cancer. 2011 Apr 15;117(8):1602-11. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25746. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21472708 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of breast cancer subtypes in elderly patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 May;157(1):91-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3787-y. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27107570 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for breast cancer brain metastases: a systematic review.Oncotarget. 2020 Feb 11;11(6):650-669. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27453. eCollection 2020 Feb 11. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32110283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic factors of brain metastasis and survival among HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients: a systematic literature review.BMC Cancer. 2021 Aug 28;21(1):967. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08708-5. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34454469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation and gene deletion analysis of brain metastases in melanoma patients identifies mutually exclusive molecular alterations.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Nov;16(11):1499-509. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou107. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24968695 Free PMC article.
-
Local control of brain metastasis: treatment outcome of focal brain treatments in relation to subtypes.J Breast Cancer. 2015 Mar;18(1):29-35. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.1.29. Epub 2015 Mar 27. J Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25834608 Free PMC article.
-
Survival outcomes of breast cancer patients with brain metastases: A multicenter retrospective study in Korea (KROG 16-12).Breast. 2020 Feb;49:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.10.007. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Breast. 2020. PMID: 31677532 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Attainability Assessment of Real-World Data for Answering Major Clinical Research Questions in Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis: Framework Development and Validation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Mar 23;25:e43359. doi: 10.2196/43359. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36951923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn HK, Lee S, Park YH, Sohn JH, Jo JC, Ahn JH, Jung KH, Park S, Cho EY, Lee JI, Park W, Choi DH, Huh SJ, Ahn JS, Kim SB, Im YH. Neuro Oncol. 2012. Prediction of outcomes for patients with brain parenchymal metastases from breast cancer (BC): a new BC-specific prognostic model and a nomogram. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duchnowska R, Dziadziuszko R, Czartoryska-Arlukowicz B, Radecka B, Szostakiewicz B, Sosinska-Mielcarek K, Karpinska A, Staroslawska E, Kubiatowski T, Szczylik C. Risk factors for brain relapse in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;117(2):297–303. doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-0275-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Graesslin O, Abdulkarim BS, Coutant C, Huguet F, Gabos Z, Hsu L, Marpeau O, Uzan S, Pusztai L, Strom EA, Hortobagyi GN, Rouzier R, Ibrahim NK. Nomogram to predict subsequent brain metastasis in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(12):2032–2037. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.6314. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

