Fine de novo sequencing of a fungal genome using only SOLiD short read data: verification on Aspergillus oryzae RIB40
- PMID: 23667655
- PMCID: PMC3646829
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063673
Fine de novo sequencing of a fungal genome using only SOLiD short read data: verification on Aspergillus oryzae RIB40
Abstract
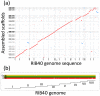
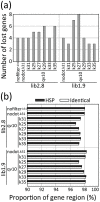
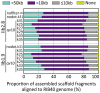
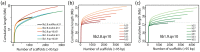
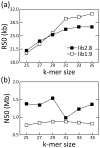
The development of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has dramatically increased the throughput, speed, and efficiency of genome sequencing. The short read data generated from NGS platforms, such as SOLiD and Illumina, are quite useful for mapping analysis. However, the SOLiD read data with lengths of <60 bp have been considered to be too short for de novo genome sequencing. Here, to investigate whether de novo sequencing of fungal genomes is possible using only SOLiD short read sequence data, we performed de novo assembly of the Aspergillus oryzae RIB40 genome using only SOLiD read data of 50 bp generated from mate-paired libraries with 2.8- or 1.9-kb insert sizes. The assembled scaffolds showed an N50 value of 1.6 Mb, a 22-fold increase than those obtained using only SOLiD short read in other published reports. In addition, almost 99% of the reference genome was accurately aligned by the assembled scaffold fragments in long lengths. The sequences of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and clusters, whose products are of considerable interest in fungal studies due to their potential medicinal, agricultural, and cosmetic properties, were also highly reconstructed in the assembled scaffolds. Based on these findings, we concluded that de novo genome sequencing using only SOLiD short reads is feasible and practical for molecular biological study of fungi. We also investigated the effect of filtering low quality data, library insert size, and k-mer size on the assembly performance, and recommend for the assembly use of mild filtered read data where the N50 was not so degraded and the library has an insert size of ∼2.0 kb, and k-mer size 33.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hybrid De Novo Genome Assembly Using MiSeq and SOLiD Short Read Data.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 28;10(4):e0126289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126289. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25919614 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudo-Sanger sequencing: massively parallel production of long and near error-free reads using NGS technology.BMC Genomics. 2013 Oct 17;14(1):711. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-711. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24134808 Free PMC article.
-
Is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? De novo assembly strategies for bacterial genomes based on paired-end sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 28;16(1):648. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1859-8. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26315384 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of short sequence reads.Brief Bioinform. 2010 Sep;11(5):457-72. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbq020. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Brief Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 20724458 Review.
-
[Genome sequencing of Aspergillus oryzae].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2006 May;51(5):452-6. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2006. PMID: 16686348 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Aspergillus oryzae as a Cell Factory: Research and Applications in Industrial Production.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Mar 26;10(4):248. doi: 10.3390/jof10040248. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of the fungal workhorses of industrial biotechnology: update on the mycotoxin and secondary metabolite potential of Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, and Trichoderma reesei.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;102(22):9481-9515. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9354-1. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30293194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Flavi and their production of aflatoxins, ochratoxins and other mycotoxins.Stud Mycol. 2019 Jun;93:1-63. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Stud Mycol. 2019. PMID: 30108412 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence- and Structure-Based Functional Annotation and Assessment of Metabolic Transporters in Aspergillus oryzae: A Representative Case Study.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8124636. doi: 10.1155/2016/8124636. Epub 2016 May 4. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27274991 Free PMC article.
-
SATRAP: SOLiD Assembler TRAnslation Program.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137436. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26368549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee SW, Markham PF, Markham JF, Petermann I, Noormohammadi AH, et al. (2011) First complete genome sequence of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. BMC Genomics 12: 197. - PubMed
-
- Perez Chaparro PJ, McCulloch JA, Cerdeira LT, Al-Dilaimi A, Canto de Sa LL, et al. (2011) Whole genome sequencing of environmental Vibrio cholerae O1 from 10 nanograms of DNA using short reads. J Microbiol Methods 87(2): 208–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

