Discovering chromatin motifs using FAIRE sequencing and the human diploid genome
- PMID: 23656909
- PMCID: PMC3655836
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-310
Discovering chromatin motifs using FAIRE sequencing and the human diploid genome
Abstract
Background: Specific chromatin structures are associated with active or inactive gene transcription. The gene regulatory elements are intrinsically dynamic and alternate between inactive and active states through the recruitment of DNA binding proteins, such as chromatin-remodeling proteins.
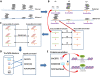
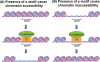
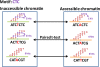
Results: We developed a unique genome-wide method to discover DNA motifs associated with chromatin accessibility using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements with high-throughput sequencing (FAIRE-seq). We aligned the FAIRE-seq reads to the GM12878 diploid genome and subsequently identified differential chromatin-state regions (DCSRs) using heterozygous SNPs. The DCSR pairs represent the locations of imbalances of chromatin accessibility between alleles and are ideal to reveal chromatin motifs that may directly modulate chromatin accessibility. In this study, we used DNA 6-10mer sequences to interrogate all DCSRs, and subsequently discovered conserved chromatin motifs with significant changes in the occurrence frequency. To investigate their likely roles in biology, we studied the annotated protein associated with each of the top ten chromatin motifs genome-wide, in the intergenic regions and in genes, respectively. As a result, we found that most of these annotated motifs are associated with chromatin remodeling, reflecting their significance in biology.
Conclusions: Our method is the first one using fully phased diploid genome and FAIRE-seq to discover motifs associated with chromatin accessibility. Our results were collected to construct the first chromatin motif database (CMD), providing the potential DNA motifs recognized by chromatin-remodeling proteins and is freely available at http://syslab.nchu.edu.tw/chromatin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global mapping of cell type-specific open chromatin by FAIRE-seq reveals the regulatory role of the NFI family in adipocyte differentiation.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002311. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22028663 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput cis-regulatory element discovery in the vector mosquito Aedes aegypti.BMC Genomics. 2016 May 10;17:341. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2468-x. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27161480 Free PMC article.
-
Global Mapping of Open Chromatin Regulatory Elements by Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements Followed by Sequencing (FAIRE-seq).Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1334:261-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2877-4_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26404156
-
Mechanisms by which transcription factors gain access to target sequence elements in chromatin.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Apr;23(2):116-23. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.11.008. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23266217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009 Nov-Dec;1(3):400-406. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.36. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20046543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin accessibility: a window into the genome.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014 Nov 20;7(1):33. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-7-33. eCollection 2014. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2014. PMID: 25473421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detect accessible chromatin using ATAC-sequencing, from principle to applications.Hereditas. 2019 Aug 15;156:29. doi: 10.1186/s41065-019-0105-9. eCollection 2019. Hereditas. 2019. PMID: 31427911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular features driving cellular complexity of human brain evolution.Nature. 2023 Aug;620(7972):145-153. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06338-4. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37468639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henikoff S. Nucleosome destabilization in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(1):15–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

