Interaction of p190RhoGAP with C-terminal domain of p120-catenin modulates endothelial cytoskeleton and permeability
- PMID: 23653363
- PMCID: PMC3689971
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432757
Interaction of p190RhoGAP with C-terminal domain of p120-catenin modulates endothelial cytoskeleton and permeability
Abstract
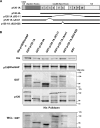
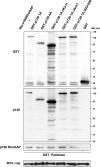
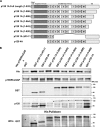
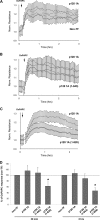
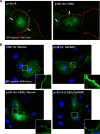
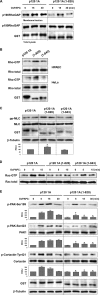
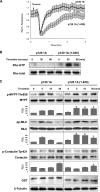
p120-catenin is a multidomain intracellular protein, which mediates a number of cellular functions, including stabilization of cell-cell transmembrane cadherin complexes as well as regulation of actin dynamics associated with barrier function, lamellipodia formation, and cell migration via modulation of the activities of small GTPAses. One mechanism involves p120 catenin interaction with Rho GTPase activating protein (p190RhoGAP), leading to p190RhoGAP recruitment to cell periphery and local inhibition of Rho activity. In this study, we have identified a stretch of 23 amino acids within the C-terminal domain of p120 catenin as the minimal sequence responsible for the recruitment of p190RhoGAP (herein referred to as CRAD; catenin-RhoGAP association domain). Expression of the p120-catenin truncated mutant lacking the CRAD in endothelial cells attenuated effects of barrier protective oxidized phospholipid, OxPAPC. This effect was accompanied by inhibition of membrane translocation of p190RhoGAP, increased Rho signaling, as well as suppressed activation of Rac1 and its cytoskeletal effectors PAK1 (p21-activated kinase 1) and cortactin. Expression of p120 catenin-truncated mutant lacking CRAD also delayed the recovery process after thrombin-induced endothelial barrier disruption. Concomitantly, RhoA activation and downstream signaling were sustained for a longer period of time, whereas Rac signaling was inhibited. These data demonstrate a critical role for p120-catenin (amino acids 820-843) domain in the p120-catenin·p190RhoGAP signaling complex assembly, membrane targeting, and stimulation of p190RhoGAP activity toward inhibition of the Rho pathway and reciprocal up-regulation of Rac signaling critical for endothelial barrier regulation.
Keywords: Adherens Junction; Catenin; Endothelial Cell; GTPase; Signal Transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of VE-cadherin controls endothelial phenotypes via p120-catenin coupling and Rac1 activation.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Jan;300(1):H162-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00650.2010. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21037229 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of endothelial cell permeability by high and low doses of oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Mar;46(3):331-41. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0153OC. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21997484 Free PMC article.
-
p120-catenin and p190RhoGAP regulate cell-cell adhesion by coordinating antagonism between Rac and Rho.Cell. 2006 Dec 1;127(5):1027-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.046. Cell. 2006. PMID: 17129786
-
p120 catenin: an essential regulator of cadherin stability, adhesion-induced signaling, and cancer progression.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;116:409-32. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394311-8.00018-2. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23481205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression of a Classic Cadherin Directs Tissue-Level Contractile Asymmetry during Neural Tube Closure.Dev Cell. 2019 Oct 21;51(2):158-172.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.001. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 31639367 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell signaling and ventilator-induced lung injury: molecular mechanisms, genomic analyses, and therapeutic targets.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):L452-L476. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00231.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27979857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic contacts: rearranging adherens junctions to drive epithelial remodelling.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;15(6):397-410. doi: 10.1038/nrm3802. Epub 2014 May 14. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24824068 Review.
-
DOCK4 Regulation of Rho GTPases Mediates Pulmonary Vascular Barrier Function.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022 Jul;42(7):886-902. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.317565. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022. PMID: 35477279 Free PMC article.
-
p190RhoGAPs, the ARHGAP35- and ARHGAP5-Encoded Proteins, in Health and Disease.Cells. 2019 Apr 12;8(4):351. doi: 10.3390/cells8040351. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31013840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ishiyama N., Lee S. H., Liu S., Li G. Y., Smith M. J., Reichardt L. F., Ikura M. (2010) Dynamic and static interactions between p120 catenin and E-cadherin regulate the stability of cell-cell adhesion. Cell 141, 117–128 - PubMed
-
- Xiao K., Oas R. G., Chiasson C. M., Kowalczyk A. P. (2007) Role of p120-catenin in cadherin trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773, 8–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

