Maternal-fetal transfer of selenium in the mouse
- PMID: 23651543
- PMCID: PMC3714584
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.13-231852
Maternal-fetal transfer of selenium in the mouse
Abstract
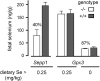
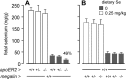
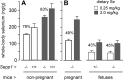
Selenoprotein P (Sepp1) is taken up by receptor-mediated endocytosis for its selenium. The other extracellular selenoprotein, glutathione peroxidase-3 (Gpx3), has not been shown to transport selenium. Mice with genetic alterations of Sepp1, the Sepp1 receptors apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (apoER2) and megalin, and Gpx3 were used to investigate maternal-fetal selenium transfer. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) showed receptor-independent uptake of Sepp1 and Gpx3 in the same vesicles of d-13 visceral yolk sac cells, suggesting uptake by pinocytosis. ICC also showed apoER2-mediated uptake of maternal Sepp1 in the d-18 placenta. Thus, two selenoprotein-dependent maternal-fetal selenium transfer mechanisms were identified. Selenium was quantified in d-18 fetuses with the mechanisms disrupted. Maternal Sepp1 deletion, which lowers maternal whole-body selenium, decreased fetal selenium under selenium-adequate conditions but deletion of fetal apoER2 did not. Fetal apoER2 deletion did decrease fetal selenium, by 51%, under selenium-deficient conditions, verifying function of the placental Sepp1-apoER2 mechanism. Maternal Gpx3 deletion decreased fetal selenium, by 13%, but only under selenium-deficient conditions. These findings indicate that the selenoprotein uptake mechanisms ensure selenium transfer to the fetus under selenium-deficient conditions. The failure of their disruptions (apoER2 deletion, Gpx3 deletion) to affect fetal selenium under selenium-adequate conditions indicates the existence of an additional maternal-fetal selenium transfer mechanism.
Keywords: apolipoprotein E receptor-2; glutathione peroxidase-3; placenta; selenoprotein P; visceral yolk sac.
Figures

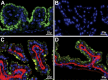
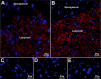
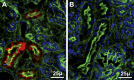
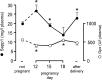
Similar articles
-
Selenoprotein P and apolipoprotein E receptor-2 interact at the blood-brain barrier and also within the brain to maintain an essential selenium pool that protects against neurodegeneration.FASEB J. 2014 Aug;28(8):3579-88. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-252874. Epub 2014 Apr 23. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24760755 Free PMC article.
-
Long isoform mouse selenoprotein P (Sepp1) supplies rat myoblast L8 cells with selenium via endocytosis mediated by heparin binding properties and apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (ApoER2).J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28717-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.383521. Epub 2012 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22761431 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoprotein P is the major selenium transport protein in mouse milk.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 28;9(7):e103486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103486. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25068390 Free PMC article.
-
SeP, ApoER2 and megalin as necessary factors to maintain Se homeostasis in mammals.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012 Oct;26(4):262-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22683052 Review.
-
Selenoprotein P-expression, functions, and roles in mammals.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Nov;1790(11):1441-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.026. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19345254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of BSA-Stabilized Selenium Nanoparticles and Sodium Selenite Supplementation on the Structure, Oxidative Stress Parameters and Selenium Redox Biology in Rat Placenta.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 28;23(21):13068. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113068. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361856 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in copper and selenium metabolism between Angus (Bos taurus) and Brahman (Bos indicus) cattle.J Anim Sci. 2021 Mar 1;99(3):skab048. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab048. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 33585942 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of low-dose selenium on thyroid autoimmunity and thyroid function in UK pregnant women with mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Feb;55(1):55-61. doi: 10.1007/s00394-014-0822-9. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25524327 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Selenium, Selenoproteins, and Female Reproduction: A Review.Molecules. 2018 Nov 22;23(12):3053. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123053. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30469536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenoprotein P and apolipoprotein E receptor-2 interact at the blood-brain barrier and also within the brain to maintain an essential selenium pool that protects against neurodegeneration.FASEB J. 2014 Aug;28(8):3579-88. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-252874. Epub 2014 Apr 23. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24760755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olson G. E., Whitin J. C., Hill K. E., Winfrey V. P., Motley A. K., Austin L. M., Deal J., Cohen H. J., Burk R. F. (2010) Extracellular glutathione peroxidase (Gpx3) binds specifically to basement membranes of mouse renal cortex tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 298, F1244–F1253 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ma S., Hill K. E., Caprioli R. M., Burk R. F. (2002) Mass spectrometric characterization of full-length rat selenoprotein P and three isoforms shortened at the C terminus. Evidence that three UGA codons in the mRNA open reading frame have alternative functions of specifying selenocysteine insertion or translation termination. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 12749–12754 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

